Alterations in the Morphology of the Testis and Epididymis Caused by the Consumption of Hyperlipidic Diets in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 40566611
- PMCID: PMC12193828
- DOI: 10.3390/life15060959
Alterations in the Morphology of the Testis and Epididymis Caused by the Consumption of Hyperlipidic Diets in Wistar Rats
Abstract
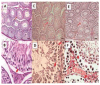
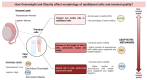
Obesity is considered a metabolic disease, in which leptin is used as an indicator of energy in the body. This hormone, in turn, is related to the neuroendocrine regulation of the reproductive axis. However, leptin excess secretion due to obesity can have a negative effect on reproduction. Overweight and obesity were induced through high-calorie diets. Lee and gonadosomatic indices were determined to characterize the model and degree of reproductive development in the testis and epididymis. Sperm quality was analyzed using spermatobioscopy. Morphometry was analyzed through histological analysis. The changes described affect testicular function in hormone and sperm production. Exposure of 3-month-old male rats to diets with different fat contents (10% and 60%) induced both overweight and obesity. The animals showed morphological alterations, both testicular and epididymal, the latter being more sensitive to dietary changes by modifying the epididymal index, morphometric parameters (in both organs), and a decrease in cilia length. These changes induced a reduction in sperm viability, as well as an increase in malformed spermatozoa. In conclusion, both overweight and obesity have effects on male reproduction by modifying the morphology and physiology of reproductive organs.
Keywords: epididymis; histomorphometry; obesity; overweight; sperm quality; testis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WITHDRAWN: Advice on low-fat diets for obesity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;2008(3):CD003640. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003640.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646093 Free PMC article.
-
Advice on low-fat diets for obesity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(2):CD003640. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003640. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD003640. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003640.pub2. PMID: 12076496 Updated.
-
Weight loss interventions for chronic asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;2012(7):CD009339. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009339.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22786526 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for weight reduction in obesity to improve survival in women with endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 27;3(3):CD012513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012513.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36971688 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for patients and caregivers to improve knowledge of sickle cell disease and recognition of its related complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 6;10(10):CD011175. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011175.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27711980 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

