[Development of a balloon sensor device for force-electrical coupling measurement of esophagus]
- PMID: 40566785
- PMCID: PMC12236215
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202404019
[Development of a balloon sensor device for force-electrical coupling measurement of esophagus]
Abstract
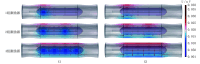
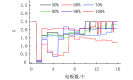
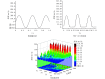
To address the challenges of capturing micro-strains in detecting esophageal motility disorders and the limitations of existing high-resolution manometry and functional intraluminal imaging probes in directly measuring esophageal tissue electrical impedance, this study proposes a novel flexible balloon sensor structure that integrates a piezoelectric film assembly with a distributed impedance electrode array. Using the electrical analysis module in the finite element analysis (FEA) software, simulations of the forward problem for esophageal impedance detection were conducted to optimize the excitation source parameters, and a physical prototype was fabricated. Under a relative excitation mode with a voltage sensitivity of 2.059%, the voltage output characteristics of the impedance electrode array were analyzed during linear changes in the balloon filling volume. Based on the performance variation of the piezoelectric film assembly, 80% was selected as the optimal filling volume. Force-electric coupling tests were conducted on the balloon sensor using a pressure testing platform, revealing that both the piezoelectric film assembly inside the balloon and the impedance electrodes outside the balloon exhibited significant load differentiation characteristics as the force application point shifted. In summary, this balloon sensor facilitates the localization of force application while simultaneously analyzing esophageal tissue properties, offering a novel diagnostic approach and objective tool for esophageal disease detection.
针对生物食管动力障碍检测中微应变难以捕捉,以及现有高分辨率测压法和功能性腔内成像探针无法直接检测食管组织电阻抗信息的问题,本研究提出了一种结合压电薄膜组和分布式阻抗电极阵列的新型柔性球囊传感器结构,借助有限元计算软件的电分析模块进行食管电阻抗检测正问题仿真,优化激励源参数,并制作实物。在电压灵敏度达到2.059%的相对激励模式下,分析了阻抗电极阵列在球囊充盈度线性变化下的电压输出特征,并结合压电薄膜组的性能变化选取80%作为最佳充盈度。本研究通过压力测试平台对球囊传感器进行力电耦合特征测试,结果表明:随着受力点的推移,囊内压电薄膜组和囊外阻抗电极的输出波均具有显著的载荷区分特性。综上,本文开发的球囊传感器有利于在区分受力位置的同时分析食管组织特性,可为食管疾病检测提供一种新的检测思路和客观的检测工具。.
Keywords: Electrical impedance measurement; Flexible balloon sensor; Force-electric coupling measurement; Polyvinylidene fluoride.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:本文全体作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures






Similar articles
-
Electrical rejuvenation of chronically implanted macroelectrodes in nonhuman primates.J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 27;21(3):10.1088/1741-2552/ad5703. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad5703. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 38862007 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of the VFSS Esophageal Screen to High-Resolution Esophageal Manometry.Laryngoscope. 2025 Jul;135(7):2283-2290. doi: 10.1002/lary.32157. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Laryngoscope. 2025. PMID: 40156431
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Choosing the right electrode representation for modeling real bioelectronic interfaces: a comprehensive guide.J Neural Eng. 2024 Aug 14;21(4). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad6a8b. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 39094614
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
