Associations between objective sleep metrics and brain structure in cognitively unimpaired adults: interactions with sex and Alzheimer's biomarkers
- PMID: 40566790
- PMCID: PMC12198473
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70353
Associations between objective sleep metrics and brain structure in cognitively unimpaired adults: interactions with sex and Alzheimer's biomarkers
Abstract
Introduction: Sleep disturbances are prevalent in Alzheimer's disease (AD), probably emerging during its preclinical stage. Poor subjective sleep quality is linked to reduced brain volume and cortical thickness (CTh), but associations with objective sleep measures, particularly regarding sex and AD pathology, remain unclear.
Methods: We characterized 171 cognitively unimpaired adults from the ALzheimer and FAmilies (ALFA) Sleep study using actigraphy, MRI, amyloid beta 42/40, and phosphorylated tau at threonine 181 in cerebrospinal fluid.
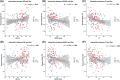
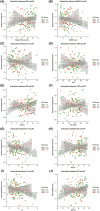
Results: Lower sleep efficiency, higher wake after sleep onset (WASO), and sleep fragmentation were associated with lower CTh in the medial temporal lobe and other regions linked with AD and sleep disruption, even after adjusting for AD biomarkers. Sex and AD biomarkers modified these associations, with longer WASO showing a stronger correlation with lower CTh in females.
Discussion: Disrupted sleep may reduce cortical integrity independently of AD biomarkers, suggesting alternative pathways. Females appear more vulnerable to impaired sleep, and AD pathology may exacerbate AD-related changes in CTh.
Highlights: Poor sleep efficiency, increased WASO, and sleep fragmentation are associated with reduced CTh in regions vulnerable to early AD, independently of amyloid and tau pathology. In the presence of AD pathology, this relationship is altered, with A+T+ individuals exhibiting increased CTh associated with sleep disruption. Sex-specific effects suggest females are more vulnerable to sleep-related cortical thinning. These findings highlight the potential of targeting sleep as a secondary prevention strategy to preserve brain integrity and mitigate neurodegenerative processes in AD-vulnerable regions.
Keywords: actigraphy; cortical thickness; preclinical AD; sex differences; sleep.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
O.G.R. receives research funding from F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd. and has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Roche Diagnostics, S.L.U. G.S‐B. worked as a consultant for Roche Farma, S.A. M.S‐C. has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Almirall, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, and Roche Farma; received consultancy fees (paid to the institution) from Roche Diagnostics; and served on advisory boards of Eli Lilly, Grifols, and Roche Diagnostics. He was granted a project and is a site investigator of a clinical trial (funded to the institution) by Roche Diagnostics. In‐kind support for research (to the institution) was received from ADx Neurosciences, Alamar Biosciences, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Janssen Research & Development, and Roche Diagnostics. H.Z. has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Alzecure, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). K.B. has served as a consultant and on advisory boards for Acumen, ALZPath, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Lilly, Moleac Pte. Ltd., Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served on data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials, and participated in educational programs for AC Immune, Biogen, Celdara Medical, Eisai, and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. J.D.G. receives research funding from Roche Diagnostics and GE Healthcare, has given lectures at symposia sponsored by Biogen and Philips, and is currently an employee of AstraZeneca. J.L.M. is currently a full‐time employee of Lundbeck and previously served as a consultant or on advisory boards for the following for‐profit companies or has given lectures in symposia sponsored by the following for‐profit companies: Roche Diagnostics, Genentech, Novartis, Lundbeck, Oryzon, Biogen, Lilly, Janssen, Green Valley, MSD, Eisai, Alector, BioCross, GE Healthcare, and ProMISNeurosciences. The NeuroToolKit is a panel of exploratory prototype assays designed to robustly evaluate biomarkers associated with key pathologic events characteristic of AD and other neurological disorders, used for research purposes only and not approved for clinical use (Roche Diagnostics International Ltd., Rotkreuz, Switzerland). Elecsys Phospho‐Tau (181P) CSF and Elecsys Total‐Tau CSF immunoassays are approved for clinical use. ELECSYS is a trademark of Roche. The rest of the coauthors have nothing to disclose. S.C.H., T.M., and P.G. are employees of F. Hoffmann‐La Roche Ltd. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- LCF/BQ/PR21/11840004/Marie Skłodowska-Curie
- 100010434/'la Caixa' Foundation
- 2017-SGR-892/Catalan Government
- PI22/00456/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- RYC‑2013‑13054/Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation
- Universities and Research Secretariat
- ZEN‑21‑848495/Alzheimer's Association 2021 Zenith
- Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor
- ADSF-21-831377-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- 115952/EU/EFPIA Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking AMYPAD
- PI19/00117/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- ERC_/European Research Council/International
- Olav Thon Foundation
- JPND2019‑466‑236/European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders
- LCF/PR/GN17/50300004/'la Caixa' Foundation
- 2017‑00915/Swedish Research Council
- TriBEKa‑17‑519007/TriBEKa Imaging Platform project
- 2019-AARF-644568/Alzheimer's Association Research Fellowship Program
- AF‑742881/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- Swedish government and the County Councils
- R01 AG068398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EU's Horizon 2020
- Bluefield Project
- 860197/Marie Skłodowska-Curie
- ALFGBG‑715986/ALF‑agreement
- Ministry of Business and Knowledge
- ADSF-21-831381-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- RDAPB‑201809‑2016615/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- 948677/European Union's Horizon
- FO2017‑0243/Hjärnfonden
- ADSF-21-831376-C/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- AD Strategic Fund
- PID2020-119556RA-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovacion, Spanish Research Agency
- IJC2020-043417-I/Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities
- 847648/Marie Skłodowska-Curie
- ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- JPND2021-00694/European Union Joint Programme - Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- 1R01AG068398‑01/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 101053962/European Union's Horizon Europe
- UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute
- 2021/EIT Digital
- 201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- RTI2018‑102261/Ministerio de Ciencia y Universidades
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

