Biology and utilization of R2 retrotransposons
- PMID: 40566873
- PMCID: PMC12203849
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2521890
Biology and utilization of R2 retrotransposons
Abstract
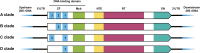
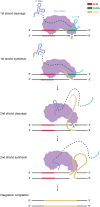
R2 elements serve as a class of non-long terminal repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposons found in animal genomes that specifically insert into the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequences of host genomes. Each R2 element contains a single open reading frame (ORF) encoding a multifunctional protein with nucleic acid-binding, reverse transcriptase, and endonuclease activities, enabling specific genomic integration via a mechanism called target-primed reverse transcription (TPRT). As a classical model for studying retrotransposition mechanisms, R2 elements possess unique biological properties and precise integration capabilities, which have inspired novel genome engineering strategies. In this review, we summarize the components and integration mechanisms of R2 retrotransposons and highlight the recent advances in employing these mobile elements for targeted gene integration. Finally, we present future directions for the utilization of R2 retrotransposons as novel biotechnological tools.
Keywords: R2 retrotransposons; RNA; gene integration; genome engineering; mechanism; protein domains; reverse transcription; ribozyme.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials