Nematode mind: exploring the role of the RNA interference pathway in learning, memory and beyond
- PMID: 40566921
- PMCID: PMC12198895
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0125
Nematode mind: exploring the role of the RNA interference pathway in learning, memory and beyond
Abstract
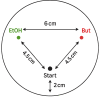
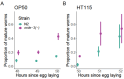
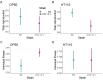
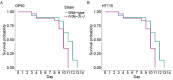
Caenorhabditis nematodes, particularly the well-known Caenorhabditis elegans, have challenged early views of them as hard-wired by demonstrating diverse learning and memory capabilities. This cognitive repertoire, developed with just several hundred neurons, highlights the evolutionary importance of cognitive traits. In this study, we examine the relationship between learning, development, reproduction and lifespan, focusing on its regulation by the conserved RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. Specifically, we examine NRDE-3, a key Argonaute protein in this pathway using an RNAi-defective nrde-3 mutant to evaluate the effects of this mutation under two diets. Consistent with previous findings, nrde-3 mutants exhibited a trend towards deteriorated aversive learning; at the same time, no decline in positive learning was observed. Additionally, we found that the nrde-3 mutant had faster development but also reduced lifespan under the stressful condition of light exposure. We propose that the RNAi pathway, alongside the target of rapamycin and insulin/insulin-like signalling pathways, contributes to the correlated evolution of learning and life-history traits. Notably, recent research has linked the RNAi pathway to the epigenetic inheritance of learned behaviours, presenting new opportunities for integrated investigations into within-generation learning and transgenerational responses. Accordingly, we suggest future research directions that take advantage of the genomic resources, biodiversity and experimental tractability of Caenorhabditis.This article is part of the Theo Murphy meeting issue 'Selection shapes diverse animal minds'.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; NRDE-3 Argonaute protein; RNA interference (RNAi); learning and memory; life-history evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Two H3K23 histone methyltransferases, SET-32 and SET-21, function synergistically to promote nuclear RNAi-mediated transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2025 Feb 5;229(2):iyae206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae206. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 39661453
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Selection shapes diverse animal minds.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;380(1929):20240108. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0108. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40566907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunlap AS, Stephens DW. 2016. Reliability, uncertainty, and costs in the evolution of animal learning. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 12, 73–79. ( 10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.09.010) - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

