Identification of New Human P2X7 Antagonists Using Ligand- and Structure-Based Virtual Screening
- PMID: 40566963
- PMCID: PMC12264943
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00552
Identification of New Human P2X7 Antagonists Using Ligand- and Structure-Based Virtual Screening
Abstract
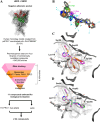
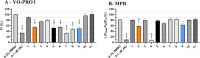
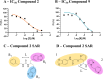
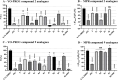
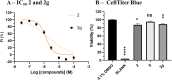
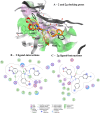
P2X7 receptors, a subtype of ATP-gated cation channel, have gained attention due to their involvement in inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases, chronic pain, and cancer. However, despite extensive medicinal chemistry efforts, no P2X7 antagonists have reached clinical approval due to suboptimal pharmacokinetic properties, poor selectivity, and insufficient efficacy in comparison to placebo controls. To address these challenges, we employed a virtual screening workflow integrating ligand-based and structure-based approaches to identify novel P2X7 allosteric antagonists. A 3D pharmacophore model derived from three known P2X7 antagonists (A740003, A804598, and JNJ47965567) was used to filter four libraries of commercially available compounds (approximately 10,000,000 total). These compounds were docked into a human P2X7 homology model and ranked by four distinct scoring functions. Eleven compounds were selected based on drug-like properties and key interactions with residues lining the target pocket. Among those, six compounds inhibited P2X7 activation in a YO-PRO 1 dye uptake assay (30 μM), while just two of those (2 and 9) were also active in a Membrane Potential Red assay (10 μM). Further screening of 10 analogues of 2 and 9 led to the identification of 2g, which displayed comparable potency (IC50 = 1.31 μM) to 2 (IC50 = 1.88 μM) in the YO-PRO 1 dye uptake assay. Docking studies of 2g within the negative allosteric pocket provided insights into its binding mode and key interacting residues. These findings offer a promising starting point for the development of optimized P2X7 antagonists.
Figures
References
-
- North R. A., Buell G.. P2X purinoceptor plethora. Semin. Neurosci. 1996;272(May):187–194. doi: 10.1006/smns.1996.0024. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

