Granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as isolated ear involvement: a case series and literature review
- PMID: 40567100
- PMCID: PMC12201922
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N3008
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as isolated ear involvement: a case series and literature review
Abstract
Objective: To describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients affected by granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) presenting with isolated ear involvement.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients affected by GPA and treated at the University of Brescia, Italy, from 2002 to 2023 was conducted. Only patients with exclusive otologic manifestation as first presentation were included.
Results: Among 610 patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) diagnosed and followed at our Institution, 6 (0.8%) presented with exclusive ear involvement as first presentation, all affected by GPA. Most frequently patients presented with otitis media with effusion, sensorineural or mixed hearing loss, and dizziness. Two patients developed systemic symptoms. All patients experienced at least a partial recovery of middle ear function after starting immunosuppressive therapy.
Conclusions: AAVs rarely show initial presentation as isolated ear involvement, and more commonly present as otitis media with hearing loss that is unresponsive to conventional therapy. Once an AAV is suspected, surgery should be avoided since further damage can be caused by local iatrogenic inflammation sustained by the underlying condition. Local improvement is generally seen after the start of immunosuppressive therapy.
Keywords: anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis; granulomatosis with polyangiitis; hearing loss; otitis media; vasculitis.
Copyright © 2025 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
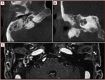
References
-
- Jennette JC, Xiao H, Falk RJ. Pathogenesis of vascular inflammation by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:1235-1242. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005101048 10.1681/ASN.2005101048 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McDonald TJ, DeRemee RA. Wegener’s granulomatosis. Laryngoscope 1983;93:220-231. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198302000-00020 10.1288/00005537-198302000-00020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wojciechowska J, KręCicki T. Clinical characteristics of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in ENT practice: a comparative analysis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2018;38:517-527. https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-1776 10.14639/0392-100X-1776 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoshida N, Hara M, Hasegawa M, et al. Reversible cochlear function with ANCA-associated vasculitis initially diagnosed by otologic symptoms. Otol Neurotol 2014;35:114-120. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000000175 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000175 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berrettini S, Ravecca F, Bruschini L, et al. Progressive sensorineural hearing loss: immunologic etiology. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 1998;18:33-41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

