Association between SGLT-2 inhibitors and suicide risk in type 2 diabetes and bipolar: a real-world cohort study
- PMID: 40567368
- PMCID: PMC12188542
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1601118
Association between SGLT-2 inhibitors and suicide risk in type 2 diabetes and bipolar: a real-world cohort study
Abstract
Background: Individuals with bipolar disorder face a significantly elevated suicide risk, and comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) further complicates their psychiatric and medical outcomes. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) have demonstrated cardiometabolic benefits in T2DM, but their impact on psychiatric outcomes remains unclear. This study investigates whether SGLT-2i use is associated with a lower risk of suicide-related events compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) in individuals with bipolar disorder and T2DM.
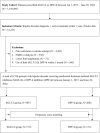
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network, a large electronic health record database. Patients were included if they had bipolar disorder, were receiving active psychiatric treatment, and initiated either SGLT-2i or DPP-4i between 1 January 2015, and 30 June 2024. The primary outcome was the occurrence of suicide-related events, including suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, or intentional self-harm. Secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, end-stage renal disease (ESRD), diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), acute kidney injury (AKI), sepsis, genital infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and lower-limb amputation. Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance baseline characteristics. Cox proportional hazards models estimated hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
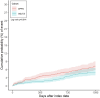
Results: The matched cohort included 1,711 patients per group (SGLT-2i vs. DPP-4i). Over a median follow-up of 887 vs. 797 days, suicide-related events occurred in 5.1% of SGLT-2i users vs. 7.3% of DPP-4i users (HR: 0.660, 95% CI: 0.473-0.921, p = 0.0145). All-cause mortality was also lower in the SGLT-2i group (HR: 0.594, 95% CI: 0.451-0.783, p < 0.001). No significant increase in adverse events such as DKA or infections was observed.
Conclusion: In this real-world cohort study, SGLT-2i use was associated with a significantly lower risk of suicide-related events and all-cause mortality compared to DPP-4i in individuals with bipolar disorder and T2DM. Subgroup analyses stratified by age, sex, race, glycemic control (HbA1c), kidney function (eGFR), and baseline lithium use revealed no evidence of increased suicide risk in any subgroup. These findings suggest that SGLT-2 inhibitors may have a neutral to potentially protective effect on suicide-related outcomes. Further prospective studies are warranted to confirm these observations and explore the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: DPP4; SGLT2; bipolar; cohort study; diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Chang, Huang, Lo, Huang, Yang and Kornelius.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucose-Lowering Medications and Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Intern Med. 2025 Apr 1;185(4):399-410. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.7811. JAMA Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39928303
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and inverse risk of new-onset atopic dermatitis in a cohort with diabetes: a nationwide active-comparator study.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):74-84. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf086. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40037684
-
Risk of bone fracture by using dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 11;15:1410883. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1410883. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39464183 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing SGLT-2 inhibitors to DPP-4 inhibitors as an add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab. 2018 Mar;44(2):112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2018.01.017. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Diabetes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29477373
-
Insulin and glucose-lowering agents for treating people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 24;9(9):CD011798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30246878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breznoscakova D., Pallayova M. (2022). Bipolar disorder and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship. Eur. J. Psychiatry 36 (3), 152–162. 10.1016/j.ejpsy.2021.11.002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous