The effect of Zuogui-Jiangtang-Yishen decoction on the intestinal flora's response to L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine in patients with diabetic kidney disease: an in vitro study
- PMID: 40567375
- PMCID: PMC12188454
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573514
The effect of Zuogui-Jiangtang-Yishen decoction on the intestinal flora's response to L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine in patients with diabetic kidney disease: an in vitro study
Abstract
Background: Animal and cell studies have demonstrated that Zuogui-Jiangtang-Yishen decoction (ZGJTYS) has a favorable effect on the treatment of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Our previous clinical research also showed that ZGJTYS prevents DKD in a manner similar to that of benazepril. Nevertheless, the interactions between ZGJTYS and the human gut microbiota require further investigation, particularly its interference in the intestinal flora response to food ingredients that may increase DKD risk, such as L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the regulatory function of ZGJTYS on human gut microbiota and explore the effect of ZGJTYS on the intestinal flora response to L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine.
Methods: ZGJTYS was prescribed from the First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine. High-throughput sequencing of bacterial 16S RNA genes and fungal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences was used for intestinal flora analysis. An in vitro gut microbiota simulation model was used to investigate the effect of ZGJTYS on the intestinal flora's response to L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry were used for non-targeted metabolomics analysis.
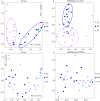
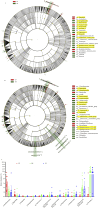
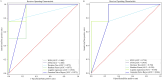
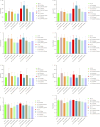
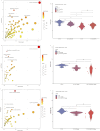
Results: Compared to the control group, the microbial diversity of DKD was significantly reduced by ZGJTYS treatment; three bacterial genera, including Parabacterioids, were significantly higher; eight bacterial genera, including Prevotella_9, and the linoleic acid content were significantly lower. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis using Parabacterioids and Prevotella_9 showed an area under the curve greater than 0.75, indicating good predictive performance. ZGJTYS intervention restored some of the normal bacterial genera, such as Rickettsia and Metarhizium, which were regulated by L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine. Furthermore, ZGJTYS effectively restored several significantly different Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes metabolic pathways related to immunity and disease to normal, such as efferocytosis and tryptophan metabolism.
Conclusion: ZGJTYS was found to effectively restore the microbiota that were altered by L-α-phosphatidylcholine and L-tyrosine to normal, along with their metabolites. However, the mechanism by which ZGJTYS exerts its preventive and therapeutic effects on DKD through the gut microbiota still requires further study.
Keywords: L-tyrosine; L-α-phosphatidylcholine; Zuogui-Jiangtang-Yishen decoction; diabetic kidney disease; in vitro fermentation; intestinal flora.
Copyright © 2025 Yin, Zhao, Xiang, Li, Liu, Hu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen C., Li F., Yu R., He-Xi Q., Tang Y., Luo W. (2015). Zuogui-Jiangtang-Yishen decoction for type 2 diabetes complicated with chronic kidney disease. Lishizhen Med. Materia Medica Res. 26 (03), 641–642.
-
- Chen C., Yu R., Wu Y., Yin H., Tang Y., Luo W., et al. (2014). Effects of Zuogui Jiangtang Yishen decoction on blood glucose, blood lipids, renal function and the serum content of IL-6, TNF-α of MKR mice with diabetic nephropathy. China J. Traditional Chin. Med. Pharm. 29 (05), 1618–1621.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

