Potential of functional flavonoids in targeting vasospasm through modulation of oxidative stress and SPC-induced signaling pathways
- PMID: 40567377
- PMCID: PMC12187668
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1594060
Potential of functional flavonoids in targeting vasospasm through modulation of oxidative stress and SPC-induced signaling pathways
Abstract
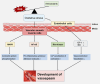
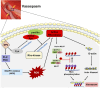
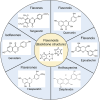
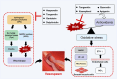
Vasospasm is a sustained abnormal contraction of vascular smooth muscle (VSM), which is commonly observed in the coronary and cerebral arteries. This abnormal VSM contraction leads to reduced blood flow to tissues or organs, ultimately causing severe diseases such as myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction. Studies have demonstrated that oxidative stress and sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC)-induced Rho-kinase signaling pathways are related to this abnormal contraction. Flavonoids, a class of natural compounds, are found in various plants, fruits, vegetables, and traditional Chinese medicines. They have anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anticarcinogenic properties. Recent studies have shown that some flavonoids strongly inhibit the abnormal contraction of VSM. This review explores the potential of flavonoids as candidate drugs for the treatment and prevention of vasospasm through oxidative stress and the SPC-induced Rho-kinase signaling pathway. Nevertheless, more extensive studies are required to fully elucidate the mechanism by which flavonoids exert their anti-vasospastic effects and explore their potential benefits as adjunctive therapy for critical cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Keywords: ROS; SPC; flavonoids; oxidative stress; vasospasm.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Maejima, Matsuzaki and Kishi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alrumaihi F., Almatroodi S. A., Alharbi H. O. A., Alwanian W. M., Alharbi F. A., Almatroudi A., et al. (2024). Pharmacological potential of kaempferol, a flavonoid in the management of pathogenesis via modulation of inflammation and other biological activities. Molecules 29, 2007. 10.3390/molecules29092007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

