Effectiveness of Combination of Thunder Fire Moxibustion with Other Forms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Osteoarthritis Knee: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40567425
- PMCID: PMC12191181
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S502457
Effectiveness of Combination of Thunder Fire Moxibustion with Other Forms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Osteoarthritis Knee: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Given the prevalence of osteoarthritis and the growing interest in alternative treatments, there is a need to provide a comprehensive evaluation of this integrated TCM approach. Reviews are required to understand the potential benefits and safety of the combination therapy compared to conventional treatments. Hence, this meta-analysis investigates the effectiveness of combining Thunder Fire Moxibustion with other Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) modalities, specifically acupuncture and herbal formulas, in treating knee osteoarthritis.
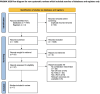
Methods: A comprehensive literature search across databases like PubMed Central, EMBASE, MEDLINE, and others was conducted. The inclusion criteria focused on randomized controlled trials involving patients with knee osteoarthritis, comparing the effectiveness of Thunder Fire Moxibustion combined with other TCM modalities against standard care. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool was used for bias assessment, and a random-effects inverse-variance model for meta-analysis.
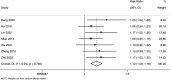
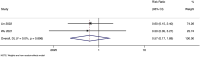
Results: Out of 1467 records, 7 studies met the inclusion criteria. The pooled Risk Ratio (RR) for total effective rate was 1.119, indicating a significant effect of the combined TCM treatment. Subgroup analysis showed a pooled RR of 1.130 for acupuncture combinations and 1.103 for herbal TCM combinations. The incidence of adverse reactions had a non-significant pooled RR of 0.572. The GRADE assessment indicated a low overall quality of evidence due to risks of bias and publication bias.
Conclusion: The combination of Thunder Fire Moxibustion with other TCM modalities shows potential effectiveness in treating knee osteoarthritis, with minimal adverse reactions. However, the low quality of evidence suggests a need for more rigorous studies to confirm these findings.
Keywords: acupuncture; meta-analysis; moxibustion; osteoarthritis.
© 2025 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Wei Wei and Yeyu Qin are co-first authors for this study. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Pharmacological treatment for antipsychotic-related constipation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 24;1(1):CD011128. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011128.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28116777 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for oesophageal cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 22;2016(1):CD004520. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004520.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26799001 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 2;12(12):CD012057. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012057.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29197180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Does Thunder-Fire Moxibustion Really Augment Therapeutic Efficacy in Knee Osteoarthritis? Methodological Critique of A Recent Pairwise Meta-Analysis [Letter].J Pain Res. 2025 Jul 23;18:3717-3722. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S551887. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40718716 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hsu H, Siwiec RM. Knee Osteoarthritis. 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507884/. Accessed June 9, 2025. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

