Functional redundancy of the posterior hippocampi is selectively disrupted in non-demented older adults with β-amyloid deposition
- PMID: 40567448
- PMCID: PMC12172829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2025.100255
Functional redundancy of the posterior hippocampi is selectively disrupted in non-demented older adults with β-amyloid deposition
Abstract
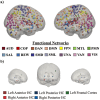
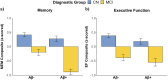
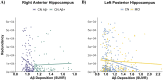
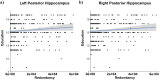
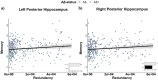
Several neural mechanisms underlying resilience to Alzheimer's disease (AD) have been proposed, including redundant neural connections between the posterior hippocampi and all other brain regions, and global functional connectivity of the left frontal cortex (LFC). Here, we investigated if functional redundancy of the hippocampus (HC) and LFC underscores neural resilience in the presence of early AD pathologies. From the ADNI database, cognitively normal older adults (CN) (N = 220; 36 % Aβ+) and patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) (N = 143; 51 % Aβ+) were utilized. Functional redundancy was calculated from resting state fMRI data using a graph theoretical approach by summing the direct and indirect paths (path lengths = 1-4) between each region of interest and its 263 functional connections. Posterior HC, but not anterior HC or LFC, redundancy was significantly lower in Aβ+ than Aβ-groups, regardless of diagnosis. Posterior HC redundancy related to higher education and better episodic memory, but it did not moderate the Aβ-cognition relationships across the diagnostic groups. Together, these findings suggest that posterior HC redundancy captures network disruption that parallels selective vulnerability to Aβ deposition. Further, our findings indicate that functional redundancy may underscore a network metric different from global functional connectivity of the LFC.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer's disease; Beta-amyloid plaques; Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Graph theory; Resilience.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting cognitive decline: Deep-learning reveals subtle brain changes in pre-MCI stage.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 May;12(5):100079. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100079. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39920001 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Vitamin E for Alzheimer's dementia and mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28418065 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperconnectivity and Connectome Gradient Dysfunction of Cerebello-Thalamo-Cortical Circuitry in Alzheimer's Disease Spectrum Disorders.Cerebellum. 2025 Feb 6;24(2):43. doi: 10.1007/s12311-025-01792-4. Cerebellum. 2025. PMID: 39913059
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
