Improved salp swarm algorithm based optimization of mobile task offloading
- PMID: 40567648
- PMCID: PMC12190771
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2818
Improved salp swarm algorithm based optimization of mobile task offloading
Abstract
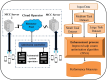
Background: The realization of computation-intensive applications such as real-time video processing, virtual/augmented reality, and face recognition becomes possible for mobile devices with the latest advances in communication technologies. This application requires complex computation for better user experience and real-time decision-making. However, the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile devices have computational power and limited energy. Executing these computational-intensive tasks on edge devices may result in high energy consumption or high computation latency. In recent times, mobile edge computing (MEC) has been used and modernized for offloading this complex task. In MEC, IoT devices transmit their tasks to edge servers, which consecutively carry out faster computation.
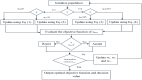
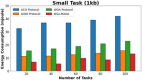
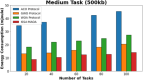
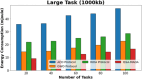
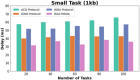
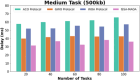
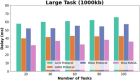
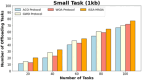
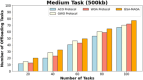
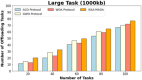
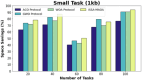
Methods: However, several IoT devices and edge servers put an upper limit on executing concurrent tasks. Furthermore, implementing a smaller size task (1 KB) over an edge server leads to improved energy consumption. Thus, there is a need to have an optimum range for task offloading so that the energy consumption and response time will be minimal. The evolutionary algorithm is the best for resolving the multiobjective task. Energy, memory, and delay reduction together with the detection of the offloading task is the multiobjective to achieve. Therefore, this study presents an improved salp swarm algorithm-based Mobile Application Offloading Algorithm (ISSA-MAOA) technique for MEC.
Results: This technique harnesses the optimization capabilities of the improved salp swarm algorithm (ISSA) to intelligently allocate computing tasks between mobile devices and the cloud, aiming to concurrently minimize energy consumption, and memory usage, and reduce task completion delays. Through the proposed ISSA-MAOA, the study endeavors to contribute to the enhancement of mobile cloud computing (MCC) frameworks, providing a more efficient and sustainable solution for offloading tasks in mobile applications. The results of this research contribute to better resource management, improved user interactions, and enhanced efficiency in MCC environments.
Keywords: Cloud computing; Mobile application offloading; Mobile edge computing; Salp swarm algorithm; Task offloading.
© 2025 R. and G.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
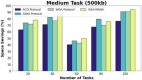
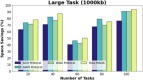
References
-
- Abbas A, Raza A, Aadil F, Maqsood M. Meta-heuristic-based offloading task optimization in mobile edge computing. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. 2021;17(6):15501477211023021. doi: 10.1177/15501477211023021. - DOI
-
- Aishwarya R, Mathivanan G. Mobile cloud offloading: an analysis of methodologies, limitations, and research problems. 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT); 2023. pp. 1–8.
-
- Aishwarya R, Mathivanan G. COCAME: a computational offloading in cloud assisted mobile environments structure to enhance performance and energy. 2024 14th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence); 2024. pp. 264–271.
-
- Al-Hammadi I, Li M, Islam SM, Al-Mosharea E. Collaborative computation offloading for scheduling emergency tasks in SDN-based mobile edge computing networks. Computer Networks. 2024;238(1):110101. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2023.110101. - DOI
-
- Bi J, Wang Z, Yuan H, Zhang J, Zhou M. Cost-minimized computation offloading and user association in hybrid cloud and edge computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2024;11(9):16672–16683. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3354348. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
