SODU2-NET: a novel deep learning-based approach for salient object detection utilizing U-NET
- PMID: 40567673
- PMCID: PMC12190711
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2623
SODU2-NET: a novel deep learning-based approach for salient object detection utilizing U-NET
Abstract
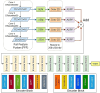
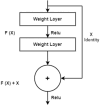
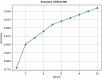
Detecting and segmenting salient objects from natural scenes, often referred to as salient object detection, has attracted great interest in computer vision. To address this challenge posed by complex backgrounds in salient object detection is crucial for advancing the field. This article proposes a novel deep learning-based architecture called SODU2-NET (Salient object detection U2-Net) for salient object detection that utilizes the U-NET base structure. This model addresses a gap in previous work that focused primarily on complex backgrounds by employing a densely supervised encoder-decoder network. The proposed SODU2-NET employs sophisticated background subtraction techniques and utilizes advanced deep learning architectures that can discern relevant foreground information when dealing with complex backgrounds. Firstly, an enriched encoder block with full feature fusion (FFF) with atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) varying dilation rates to efficiently capture multi-scale contextual information, improving salient object detection in complex backgrounds and reducing the loss of information during down-sampling. Secondly the block includes an attention module that refines the decoder, is constructed to enhances the detection of salient objects in complex backgrounds by selectively focusing attention on relevant features. This allows the model to reconstruct detailed and contextually relevant information, which is essential to determining salient objects accurately. Finally, the architecture has been improved by adding a residual block at the encoder end, which is responsible for both saliency prediction and map refinement. The proposed network is designed to learn the transformation between input images and ground truth, enabling accurate segmentation of salient object regions with clear borders and accurate prediction of fine structures. SODU2-NET is demonstrated to have superior performance in five public datasets, including DUTS, SOD, DUT OMRON, HKU-IS, PASCAL-S, and a new real world dataset, the Changsha dataset. Based on a comparative assessment of the model FCN, Squeeze-net, Deep Lab, Mask R-CNN the proposed SODU2-NET is found and achieve an improvement of precision (6%), recall (5%) and accuracy (3%). Overall, approach shows promise for improving the accuracy and efficiency of salient object detection in a variety of settings.
Keywords: ASPP module; Attention mechanism; Deep learning; Salient object detection; U-Net.
© 2025 Abbas et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures















Similar articles
-
Multi-level channel-spatial attention and light-weight scale-fusion network (MCSLF-Net): multi-level channel-spatial attention and light-weight scale-fusion transformer for 3D brain tumor segmentation.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6301-6325. doi: 10.21037/qims-2025-354. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727355 Free PMC article.
-
A novel image segmentation network with multi-scale and flow-guided attention for early screening of vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN).Med Phys. 2025 Aug;52(8):e18041. doi: 10.1002/mp.18041. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40804792
-
A novel recursive transformer-based U-Net architecture for enhanced multi-scale medical image segmentation.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Sep;196(Pt A):110658. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110658. Epub 2025 Jul 6. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40618700
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Aboelenein NM, Songhao P, Koubaa A, Noor A, Afifi A. HTTU-Net: hybrid two track U-Net for automatic brain tumor segmentation. IEEE Access. 2020;8:101406–101415. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2998601. - DOI
-
- Bao Y, Dai H, Elsaddik A. Semi-supervised cross-modal salient object detection with U-structure networks. 2022. ArXiv. - DOI
-
- Bello I, Fedus W, Du X, Cubuk ED, Srinivas A, Lin T-Y, Shlens J, Zoph B. Revisiting ResNets: improved training and scaling strategies. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2021;34:22614–22627. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2103.07579. - DOI
-
- Boulila W, Khlifi MK, Ammar A, Koubaa A, Benjdira B, Farah IR. A hybrid privacy-preserving deep learning approach for object classification in very high-resolution satellite images. Remote Sensing. 2022;14(18):4631. doi: 10.3390/rs14184631. - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
