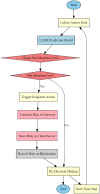
Design of an improved graph-based model integrating LSTM, LoRaWAN, and blockchain for smart agriculture
- PMID: 40567697
- PMCID: PMC12192981
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2896
Design of an improved graph-based model integrating LSTM, LoRaWAN, and blockchain for smart agriculture
Abstract
This research is anchored on the burning need for irrigation optimization and crop water use efficiency improvement, which remains a challenge in smart agriculture processes. Traditional irrigation methods normally lead to inefficiency, resulting in wasted water and non-maximum crops. These traditional ways normally lack attributes of real-time adaptability and secure data management-things that are very key to modernizing agricultural practices. In this work, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain techniques will be integrated to design a comprehensive system for monitoring and predicting soil moisture levels. In the proposed model, long short-term memory (LSTM) networks are considered for soil moisture level prediction, taking into consideration past data, weather, and crop type. LSTM networks are chosen here for their high performance in timestamp series prediction tasks with an mean average error (MAE) of 0.02 m3/m3 over a 7-day forecast horizon. For real-time monitoring, IoT sensors based on long range wide area network (LoRaWAN) technology are field-deployed for conducting long-range communications while consuming very limited energy to extend the sensor battery life over 5 years and bring down the data transmission latency below 5 s. It has an inbuilt permissioned blockchain framework-Hyperledger Fabric-which offers a secure and transparent system for data management and maintaining a record of soil moisture data, irrigation events, and metadata from sensors. This ensures the immutability and integrity of sets of data. Smart contracts automate irrigation upon reaching preconfigured soil moisture thresholds, and hence zero data integrity breaches occur with a transaction throughput of 1,000 transactions per second, taken into view with smart contract execution latency of less than 2 s. Moreover, it utilizes reinforcement learning with Deep Q-Learning to derive an optimized irrigation schedule. In this regard, it enables learning optimal irrigation policies and implements them to improve efficiency in the usage of water by 25% and increases crop yield by 15% compared to the traditional methods. Clearly from field trials, results indicate evident efficiency of the integrated system: a 20% water usage reduction and a 12% increase in crop yield within one growing season. This is rather an innovative take on irrigation practices, increasing a great deal of accuracy and sustainability for such and providing a really strong solution toward better agricultural productivity and resource management.
Keywords: Blockchain technology; IoT sensors; LSTM networks; Smart agriculture; Soil moisture prediction.
© 2025 Munaganuri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed A, Parveen I, Abdullah S, Ahmad I, Alturki N, Jamel L. Optimized data fusion with scheduled rest periods for enhanced smart agriculture via blockchain integration. IEEE Access. 2024;12:15171–15193. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3357538. - DOI
-
- Akbar JU, Kamarulzaman SF, Muzahid AJ, Rahman A, Uddin M. A comprehensive review on deep learning assisted computer vision techniques for smart greenhouse agriculture. IEEE Access. 2024;12:4485–4522. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3349418. - DOI
-
- Akbari M, Syed A, Kennedy WS. Constrained federated learning for for smart agriculture. IEEE Transactions on Machine Learning in Communications and Networking. 2023;1:277–295. doi: 10.1109/TMLCN.2023.3311749. - DOI
-
- Akbari M, Syed A, Kennedy WS, Erol-Kantarci M. AoI-aware energy-efficient SFC in UAV-aided smart agriculture using asynchronous federated learning. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society. 2024;5:1222–1242. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2024.3363132. - DOI
-
- Alotaibi M, Murad M, Tasadduq IALI, Alhuthali SAH. Anti-collision algorithm for identification in precision agriculture applications. IEEE Access. 2023;11:130197–130205. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3334636. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous