Technological trends in epidemic intelligence for infectious disease surveillance: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 40567698
- PMCID: PMC12192675
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2874
Technological trends in epidemic intelligence for infectious disease surveillance: a systematic literature review
Abstract
Background: This research focuses on improving epidemic monitoring systems by incorporating advanced technologies to enhance the surveillance of diseases more effectively than before. Considering the drawbacks associated with surveillance methods in terms of time consumption and efficiency, issues highlighted in this study includes the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in early detection, decision support and predictive modeling, big data analytics in data sharing, contact tracing and countering misinformation, Internet of Things (IoT) devices in real time disease monitoring and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI) applications and disease mapping. The increasing intricacy and regular occurrence of disease outbreaks underscore the pressing necessity for improvements in public health monitoring systems. This research delves into the developments and their utilization in detecting and handling infectious diseases while exploring how these progressions contribute to decision making and policy development, in public healthcare.
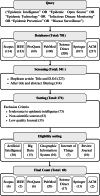
Methodology: This review systematically analyzes how technological tools are being used in epidemic monitoring by conducting a structured search across online literature databases and applying eligibility criteria to identify relevant studies on current technological trends in public health surveillance.
Results: The research reviewed 69 articles from 2019 to 2023 focusing on emerging trends in epidemic intelligence. Most of the studies emphasized the integration of artificial intelligence with technologies like big data analytics, geographic information systems, and the Internet of Things for monitoring infectious diseases.
Conclusions: The expansion of publicly accessible information on the internet has opened a new pathway for epidemic intelligence. This study emphasizes the importance of integrating information technology tools such as AI, big data analytics, GIS, and the IoT in epidemic intelligence surveillance to effectively track infectious diseases. Combining these technologies helps public health agencies in detecting and responding to health threats.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Big data; COVID-19; Epidemic intelligence; Geographic information systems; Internet of things; Public health surveillance.
© 2025 Kamarul Aryffin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Agbehadji IE, Awuzie BO, Ngowi AB, Millham RC. Review of big data analytics, artificial intelligence and nature-inspired computing models towards accurate detection of COVID-19 pandemic cases and contact tracing. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020;17(15):1–16. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155330. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed I, Ahmad M, Jeon G, Piccialli F. A framework for pandemic prediction using big data analytics. Big Data Research. 2021;25:100190. doi: 10.1016/j.bdr.2021.100190. - DOI
-
- Allam Z. Surveying the COVID-19 Pandemic and its Implications. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2020. The rise of machine intelligence in the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on health policy; pp. 89–96. - DOI
-
- Allen K. How a Toronto company used big data to predict the spread of Zika. Toronto Star. 2016. https://www.thestar.com/news/insight/how-a-toronto-company-used-big-data... https://www.thestar.com/news/insight/how-a-toronto-company-used-big-data...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources