IoT in urban development: insight into smart city applications, case studies, challenges, and future prospects
- PMID: 40567701
- PMCID: PMC12190393
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2816
IoT in urban development: insight into smart city applications, case studies, challenges, and future prospects
Abstract
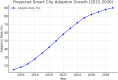
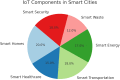
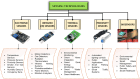
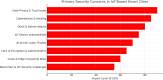
With the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, smart cities possess the capability to advance their public transportation modalities, address prevalent traffic congestion challenges, refine infrastructure, and optimize communication frameworks, thereby augmenting their progression towards heightened urbanization. Through the integration of sensors, cell phones, artificial intelligence (AI), data analytics, and cloud computing, smart cities worldwide are evolving to be more efficient, productive, and responsive to their residents' needs. While the promise of smart cities has been marked over the past decade, notable challenges, especially in the realm of security, threaten their optimal realization. This research provides a comprehensive survey on IoT in smart cities. It focuses on the IoT-based smart city components. Moreover, it provides explanation for integrating different technologies with IoT for smart cities such as AI, sensing technologies, and networking technologies. Additionally, this study provides several case studies for smart cities. In addition, this study investigates the challenges of adopting IoT in smart cities and provides prevention methods for each challenge. Moreover, this study provides future directions for the upcoming researchers. It serves as a foundational guide for stakeholders and emphasizes the pressing need for a balanced integration of innovation and safety in the smart city landscape.
Keywords: AI; IoT; Network and communication technology; Security challenges; Sensors; Smart cities.
© 2025 Salih et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Cyber-Security for Smart Cities-A Systematic Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;22(7):2792. doi: 10.3390/s22072792. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408406 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence of things for sustainable smart city brain and digital twin systems: Pioneering Environmental synergies between real-time management and predictive planning.Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2025 Jun 28;26:100591. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2025.100591. eCollection 2025 Jul. Environ Sci Ecotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40689413 Free PMC article.
-
Improved smart city security using a deep maxout network-based intrusion detection system with walrus optimization.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Mar 31;11:e2743. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2743. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40567668 Free PMC article.
-
A deep dive into artificial intelligence with enhanced optimization-based security breach detection in internet of health things enabled smart city environment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05850-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594312 Free PMC article.
-
The IoT and AI in Agriculture: The Time Is Now-A Systematic Review of Smart Sensing Technologies.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 6;25(12):3583. doi: 10.3390/s25123583. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahad MA, Paiva S, Tripathi G, Feroz N. Enabling technologies and sustainable smart cities. Sustainable Cities and Society. 2020;61(2):102301. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102301. - DOI
-
- Ahmad A, Ahmad T, Ahmad M, Kumar C, Alenezi F, Nour M. A complex network-based approach for security and governance in the smart green city. Expert Systems with Applications. 2023;214(6):119094. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119094. - DOI
-
- Ahmad K, Maabreh M, Ghaly M, Khan K, Qadir J, Al-Fuqaha A. Developing future human-centered smart cities: critical analysis of smart city security, data management, and ethical challenges. Computer Science Review. 2022;43(4):100452. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100452. - DOI
-
- Ahmadi-Assalemi G, Al-Khateeb H, Epiphaniou G, Maple C. Cyber resilience and incident response in smart cities: a systematic literature review. Smart Cities. 2020;3(3):894–927. doi: 10.3390/smartcities3030046. - DOI
-
- Akhtar W, Rahman HU, Lazoglu I. Machining process monitoring using an infrared sensor. Journal of Manufacturing Processes. 2024;131:2400–2410. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.10.063. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous