Enhancing skin lesion classification: a CNN approach with human baseline comparison
- PMID: 40567717
- PMCID: PMC12192895
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2795
Enhancing skin lesion classification: a CNN approach with human baseline comparison
Abstract
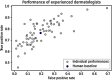
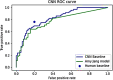
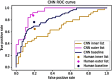
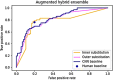
This study presents an augmented hybrid approach for improving the diagnosis of malignant skin lesions by combining convolutional neural network (CNN) predictions with selective human interventions based on prediction confidence. The algorithm retains high-confidence CNN predictions while replacing low-confidence outputs with expert human assessments to enhance diagnostic accuracy. A CNN model utilizing the EfficientNetB3 backbone is trained on datasets from the ISIC-2019 and ISIC-2020 SIIM-ISIC melanoma classification challenges and evaluated on a 150-image test set. The model's predictions are compared against assessments from 69 experienced medical professionals. Performance is assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and area under curve (AUC) metrics, alongside an analysis of human resource costs. The baseline CNN achieves an AUC of 0.822, slightly below the performance of human experts. However, the augmented hybrid approach improves the true positive rate to 0.782 and reduces the false positive rate to 0.182, delivering better diagnostic performance with minimal human involvement. This approach offers a scalable, resource-efficient solution to address variability in medical image analysis, effectively harnessing the complementary strengths of expert humans and CNNs.
Keywords: CNN; Convolutional neural networks; Deep learning; EfficientNet; EfficientNetB3; International skin imaging collaboration; International skin imaging collaboration (ISIC); Machine learning; Medical imaging; Skin cancer diagnosis.
© 2025 Ajabani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Deep Himmatbhai Ajabani is employed by Source InfoTech Inc. and Karar Ali is employed by VentureDive Pvt. Limited.
Figures
References
-
- Abadi M, Barham P, Chen J, Chen Z, Davis A, Dean J, Devin M, Ghemawat S, Irving G, Isard M, Kudlur M, Levenberg J, Monga R, Moore S, Murray DG, Steiner B, Tucker PA, Vasudevan V, Warden P, Wicke M, Yu Y, Zheng X. TensorFlow: a system for large-scale machine learning. Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 2016); Savannah, GA, USA: 2016. pp. 265–283.
-
- Abdelrahman A, Viriri S. EfficientNet family U-Net models for deep learning semantic segmentation of kidney tumors on CT images. Frontiers in Computer Science. 2023;5:1235622. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2023.1235622. - DOI
-
- Adegun A, Viriri S. Deep learning techniques for skin lesion analysis and melanoma cancer detection: a survey of state-of-the-art. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2021;54(2):811–841. doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09865-y. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources