Practical scan-length considerations for mapping upper limb movements to the somatosensory/motor cortex at 7T: A pilot study
- PMID: 40567886
- PMCID: PMC12172825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2025.100240
Practical scan-length considerations for mapping upper limb movements to the somatosensory/motor cortex at 7T: A pilot study
Abstract
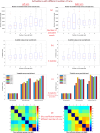
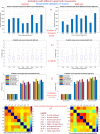
The relationship between motor cortex (M1) and upper limb movements has been investigated extensively using functional MRI (fMRI). While most research has focused on applications, very few studies have focused on practical aspects of developing the fMRI protocol. Thus, the effect of scan length on M1 activations during various upper limb movements remains unclear. Scan length constraints are important for conducting motor experiments within a 60- or 90-minute scan session. We targeted this gap in the literature in this pilot study by investigating 7T fMRI activations in a male participant while performing eight different upper limb movements (of the fingers, wrist, and elbow) across 16 task runs (8 with the left arm, 8 with the right arm, 88 minutes total fMRI duration). Standard activation analyses were performed (Z > 3.1, p < 0.01, cluster thresholded) independently for 14 different cases (2 runs through 8 runs, left and right arm) and subsequently compared. We found diminishing returns, presented as activations gradually plateauing, with higher number of runs. We observed two broad categories of movements, one with generally higher activation (more activated voxels and higher Z-stats) and the other with lower activation. To achieve similar statistical power, movements with lower activation required longer scanning (more runs). Based on these observations, we propose a 'one size does not fit all' practical protocol within a 60-, 75-, or 90- minute scan session, wherein different numbers of runs are assigned for different movements. We validated the 75-minute protocol using seven separate scans (N = 3). Our study could benefit researchers who are designing upper limb fMRI experiments.
Keywords: Activation; Fingers and thumb; Functional MRI; Somatotopic mapping; Ultra-high field; Wrist and elbow.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) for patellofemoral pain syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 12;12(12):CD011289. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011289.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29231243 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of time spent in rehabilitation on activity limitation and impairment after stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 25;10(10):CD012612. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012612.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34695300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beisteiner R., Windischberger C., Lanzenberger R., Edward V., Cunnington R., Erdler M., Gartus A., Streibl B., Moser E., Deecke L. Finger somatotopy in human motor cortex. Neuroimage. 2001;13(6 Pt 1):1016–1026. - PubMed
-
- Bican O., Minagar A., Pruitt A.A. The spinal cord: a review of functional neuroanatomy. Neurol. Clin. 2013;13(1):1–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
