Functional connectivity of subsystems of the default-mode network in patients with early psychotic symptoms
- PMID: 40567890
- PMCID: PMC12172822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2025.100248
Functional connectivity of subsystems of the default-mode network in patients with early psychotic symptoms
Abstract
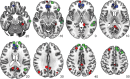
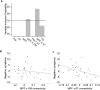
Resting-state connectivity of the default-mode network (DMN) is aberrant in patients with chronic psychotic disorders as well in individuals with early stage psychosis. Studies of the DMN in healthy volunteers revealed that the DMN comprises several subnetworks. However, it is not yet clear if connectivity between and within these DMN subnetworks is aberrant in patients with early psychotic symptoms nor whether these connectivity patterns are related to symptomatology. This initial investigation examined functional connectivity between and within the DMN subnetworks in patients with early psychotic symptoms and in healthy volunteers, and probed how these connectivity patterns were related to the severity of clinical symptomatology. Functional connectivity was measured during resting-state in 30 patients with early psychotic symptoms and in 39 controls using functional MRI. We did not observe differences in connectivity within and between the subnetworks of the DMN between the control group and the early psychosis group. However, lower functional connectivity between the medial prefrontal and posterior medial subnetworks and between medial prefrontal and anterior temporal subnetworks of the DMN did predict the severity of the negative symptoms. The findings of this initial investigation provide insight into the associations between functional connectivity of DMN subnetworks and symptomatology in patients with early psychotic symptoms.
Keywords: Default mode network; Functional connectivity; Psychosis; Psychotic symptoms; Resting-state.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Affective dysfunction mediates the link between neuroimmune markers and the default mode network functional connectivity, and the somatic symptoms in somatic symptom disorder.Brain Behav Immun. 2024 May;118:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.02.017. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Brain Behav Immun. 2024. PMID: 38360374
-
Effective connectivity of default mode network subsystems and automatic smoking behaviour among males.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2024 Dec 17;49(6):E429-E439. doi: 10.1503/jpn.240058. Print 2024 Nov-Dec. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39689937 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the effective connectivity between the anti-NMDAR encephalitis default mode network and the medial temporal lobe network using spectral dynamic causal modelling.Brain Imaging Behav. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s11682-025-01041-6. Online ahead of print. Brain Imaging Behav. 2025. PMID: 40670863
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(18):iii-iv, ix-163. doi: 10.3310/hta12180. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462577
-
The Default Mode Network in Healthy Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Brain Connect. 2017 Feb;7(1):25-33. doi: 10.1089/brain.2016.0438. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Brain Connect. 2017. PMID: 27917679
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
