Which factors affect anxiety in rural older adults in China?
- PMID: 40567968
- PMCID: PMC12187647
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1563505
Which factors affect anxiety in rural older adults in China?
Abstract
Objective: To explore the influencing factors of individual anxiety in rural older adults in China and analyze the relative importance of each factor, so as to provide scientific basis for the development of intervention measures to improve the mental health of rural older adults. The study also aims to improve the well-being and quality of life of older adults.
Methods: A multi-stage cluster random sampling was conducted in rural Anhui Province, China from July 2023 to February 2024, involving a total of 1,546 older adults. T test, ANOVA test, multiple linear regression and random forest algorithm were used for analysis.
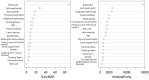
Results: The mean anxiety score among rural older adults was 4.23 ± 5.30, and the detection rate of anxiety was 36.40%. Multiple linear regression results revealed that age, marital status, visual condition, self-rated health, physical examination, consumption of coarse grains, sleep quality, subjective well-being and social support level were the influencing factors of anxiety in the older adults. The results of random forest analysis showed that depression, self-rated health, subjective well-being, sleep quality and visual acuity had great influence on anxiety in the older adults.
Conclusion: This study confirmed the influence of multiple factors on the anxiety of rural older adults. In addition, the study also found that consumption of coarse grains was negatively associated with anxiety in older adults. In order to improve the mental health of the older adults in rural areas, it is recommended to pay more attention to the older adults with depression, poor sleep quality and poor eyesight, and implement multi-dimensional intervention to improve the happiness of the older adults.
Keywords: anxiety; coarse grains consumption; older adults; random forests; visual condition.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Li, Liu, Yuan, Chen and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ju H, Jing H, Qiqun T, Jie C, Xueqi G. The relationship between anxiety and health-related quality of life among the elderly in nursing homes. Med Soc. (2022) 35:130–4+44. doi: 10.13723/j.yxysh.2022.07.024 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical