Global, regional, and national prevalence of prostate cancer from 1990 to 2021: a trend and health inequality analyses
- PMID: 40567976
- PMCID: PMC12187607
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1595159
Global, regional, and national prevalence of prostate cancer from 1990 to 2021: a trend and health inequality analyses
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer in men's health has become a significant driver of global disease burden, impacting aging populations worldwide. This study assesses its prevalence from 1990 to 2021 to reveal ongoing epidemiological trends and inform effective public health strategies.
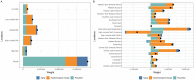
Methods: Prostate cancer prevalence estimates, including their 95% uncertainty intervals (UIs), were derived from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study. Then, temporal trends spanning the past 32 years were thoroughly analyzed using Joinpoint regression, with projections for the next 25 years made using the Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) model. Concurrently, disease trends were decomposed into components of population growth, aging, and epidemiological changes. Additionally, age-period-cohort (APC) models were also employed to explore the impact of age, time, and cohort effect on the relative risk of prostate cancer prevalence. And the cross-country inequalities in the prevalence of prostate cancer burden were meticulously evaluated through the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI), revealing significant disparities across socio-economic strata.
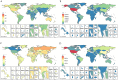
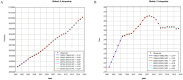
Result: In 2021, over 10 million prostate cancer cases were recorded worldwide-a 188.85% increase from 3.6 million in 1990. The age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) rose at an estimated annual percentage change of 0.64% (95% UI: 0.47%-0.82%); Joinpoint regression revealed a steady increase in case numbers over 32 years, while the ASPR peaked and then slightly declined. Decomposition analysis showed population growth as the main driver (65.62%), with epidemiological changes and aging accounting for 17.97 and 16.41%, respectively. APC modeling indicated the highest relative risk around age 75-nearly 10 times that of the general population (RR: 9.99; 95% CI: 9.97-10.01). Projections through 2046 forecast a continued rise in both total cases and ASPR.
Conclusions: As a major health concern among older adult men, the global prevalence of prostate cancer has risen steadily since 1990, with population growth identified as the primary driver. Moreover, SDI-related disparities across 204 countries and territories have widened over time. Finally, the APC model forecasts a continuous increase in prevalence over the next 25 years, underscoring the growing disease burden and the urgent need for more targeted and effective management strategies.
Keywords: Global Burden of Disease study 2021; health inequality; national; prevalence; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Liu, Zou and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

