Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Suspected Sepsis: Impact of Gentamicin-Based Regimens on Incident Renal Failure and Mortality
- PMID: 40568002
- PMCID: PMC12188214
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf319
Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Suspected Sepsis: Impact of Gentamicin-Based Regimens on Incident Renal Failure and Mortality
Abstract
Background: The efficacy and safety of administering a narrow-spectrum β-lactam and gentamicin as empirical therapy for community-acquired sepsis has been questioned. We compared the efficacy and safety of this combination with that of broad-spectrum β-lactams (cefotaxime, piperacillin-tazobactam, or meropenem) in patients with suspected sepsis.
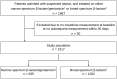
Methods: In this retrospective study, we included patients initiated on narrow-spectrum β-lactam/gentamicin or broad-spectrum β-lactams for suspected sepsis between January 2017 and December 2022. Patients without baseline creatinine and at least 1 subsequent creatinine measurement were excluded. We compared the impact of antibiotic regimens using a 5-level ordinal outcome scale ranging from no acute kidney injury (AKI) to all-cause death during 30-day follow-up.
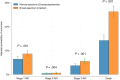
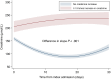
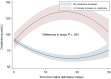
Results: Among 1917 patients, 33.1% received narrow-spectrum β-lactam/gentamicin, and 66.9% received broad-spectrum β-lactams. Patients initiated on broad-spectrum β-lactams had more comorbidities, had lower estimated glomerular filtration rate on admission, and more frequently required treatment with noradrenaline, respiratory support, and admission to the intensive care and medical intermediate care units. Therapy with broad-spectrum β-lactams was associated with a higher posttreatment stage of AKI or death (adjusted odds ratio, 1.61 [95% confidence interval, 1.27-2.04]). We found no significant association between cumulative dose of gentamicin and peak creatinine value. For patients treated with gentamicin experiencing AKI, creatinine normalized during 30-day follow-up.
Conclusions: In patients with suspected sepsis, empirical treatment with narrow-spectrum β-lactam/gentamicin was not associated with an increased risk of AKI or death. If local antimicrobial resistance patterns permit, narrow-spectrum β-lactam/gentamicin may reduce broad-spectrum β-lactam usage, addressing a key element of antibiotic stewardship.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial stewardship; mortality; nephrotoxicity; sepsis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med 2021; 49:e1063–143. - PubMed
-
- NORM/NORM-VET 2023. Usage of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in Norway. Tromsø/Ås/Oslo. 2024.
-
- Norwegian Directorate of Health. National guidelines for use of antimicrobial agents in hospitals. Oslo, Norway: Norwegian Directorate of Health, 2013.
-
- National Center for Antibiotic Use in Hospitals. Procedure aminoglycosides for adults. Bergen, Norway: National Center for Antibiotic Use in Hospitals, 2023.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

