Stigmas in Epilepsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40568055
- PMCID: PMC12185920
- DOI: 10.14581/jer.25003
Stigmas in Epilepsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
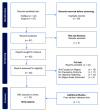
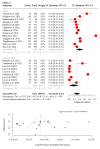
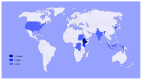
Recent research has disclosed significant associations between stigma suffered by people living with epilepsy (PWE) and psychiatric conditions, especially major depression. These results have practical implication when coupled with the precise regional-and-local prevalences of stigma in its heterogeneous manifestations among PWE. Here we review current research involving stigma in PWE to assess its prevalence and explore psychopathological associations. A systematic review was conducted in PubMed and Scopus to identify clinical trials objectively evaluating prevalence of any type of stigma, enacted and perceived, in PWE, published from database inception to 31 May 2024. A random effects meta-analysis was undertaken, with 6,072 participants, to obtain the meta-prevalence of stigma among PWE. Subgroup analysis moderated by major continent was delineated. A report was obtained from clinical documentation review and adjoined to the evidence generated. From the 105 records identified, 22 studies were eligible for inclusion. The meta-analysis revealed an overall stigma prevalence of 35% (29%; 41%), and subgroups, Africa or Asia (mostly); arbitrarily defined after analysis of geographical study distributions; indicated a prevalence of 40% (34%; 46%) and 28% (21%; 37%), respectively. Significant difference was identified (p=0.03). The case reported exemplifies how stigma may impair development, especially in children and adolescents. Stigmas among PWE are prevalent. More than one in three PWE has already experienced some form of stigma and there is potential to undermine quality of life and associate with psychiatric disorders. PWE may benefit from tailored screening and management approaches to decrease stigma burden.
Keywords: Epilepsy; Meta-analysis; Social stigma.
Copyright © 2025 Korean Epilepsy Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no financial or non-financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Lancet From wonder and fear: make epilepsy a global health priority. Lancet. 2019;393:612. - PubMed
-
- Gabriel D, Ventura M, Samões R, et al. 2020 social impairment and stigma in genetic generalized epilepsies. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;104:106886. - PubMed
-
- Lee SA, Han SH, Cho YJ, et al. Does the new Korean term for epilepsy reduce the stigma for Korean adults with epilepsy? Epilepsy Behav. 2020;102:106719. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

