The Treatment Response and Safety Profile for Mirabegron in Women With Overactive Bladder and Hypertension
- PMID: 40568251
- PMCID: PMC12197316
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84855
The Treatment Response and Safety Profile for Mirabegron in Women With Overactive Bladder and Hypertension
Abstract
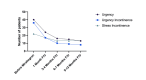
Background and objective Mirabegron, an established treatment for overactive bladder (OAB), is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Inevitably, there is concern among clinicians and patients regarding its use in patients with well-controlled hypertension. In this study, we aimed to investigate the efficacy of mirabegron in patients with well-controlled hypertension, as well as its adverse effects. Methods This retrospective study involved women with well-controlled hypertension who used mirabegron for the treatment of OAB between August 1, 2017, to July 31, 2020. Medical notes were reviewed from the time of initiation of mirabegron up to 12 months post-treatment. The indicators of response measured were frequency of maturation and nocturia. The sense of urgency and urge incontinence were assessed as well. Safety of the drug was evaluated by documenting the number of hypertensive episodes and recording side effects such as dry mouth, dry eyes, headache, and rashes. Results Forty-six patients with OAB and hypertension were included in the study. Of them, 38 patients (73.6%) had improvement in OAB symptoms following mirabegron therapy. Median urinary frequency improved from 1.5 hours to two hours after mirabegron treatment. Twenty-three of the patients stopped experiencing nocturia one month after starting mirabegron. Sixteen patients (76.2%) experienced improvement in urge symptoms while 19 patients (86.4%) experienced improvement in urge incontinence. Of note, 38 patients (78.2%) did not experience any side effects at all, while a small proportion of the patients (n=4, 8.7%) experienced anticholinergic side effects. Three patients (6.5%) experienced an increase in blood pressure after mirabegron use; no additional anti-hypertensive agents were used as mirabegron was stopped once an increase in blood pressure was noted. Conclusions Mirabegron is efficacious in improving OAB symptoms. It is well tolerated by hypertensive patients and may be used in the long term for symptom control. Home blood pressure monitoring may aid in the earlier detection of worsening control in the small segment of patients in whom mirabegron is not suitable.
Keywords: beta-3-agonist; bladder training; hypertensive patients; menopause; mirabegron; mixed urinary incontinence; overactive bladder; stress urinary incontinence; urge urinary incontinence; β3-adrenergic receptor agonist.
Copyright © 2025, Neo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. SingHealth CIRB-Board D issued approval 2019-2692. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acupuncture for treating overactive bladder in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 23;9(9):CD013519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36148895 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder training for treating overactive bladder in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 9;10(10):CD013571. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013571.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37811598 Free PMC article.
-
Anticholinergic drugs versus non-drug active therapies for non-neurogenic overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD003193. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003193.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235594 Free PMC article.
-
Which anticholinergic drug for overactive bladder symptoms in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD005429. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005429.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258963
-
Electrical stimulation with non-implanted electrodes for overactive bladder in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Dec 9;12(12):CD010098. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010098.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27935011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mirabegron in overactive bladder: a review of efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Chapple CR, Cardozo L, Nitti VW, Siddiqui E, Michel MC. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014;33:17–30. - PubMed
-
- Home blood pressure monitoring is a better predictor of cardiovascular disease and target organ damage than office blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fuchs SC, Mello RG, Fuchs FC. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2013;15:413. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources