Inflammation and dyslipidaemia in combined diabetes and tuberculosis; a cohort study
- PMID: 40568317
- PMCID: PMC12192345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112760
Inflammation and dyslipidaemia in combined diabetes and tuberculosis; a cohort study
Abstract
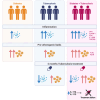
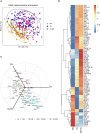
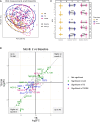
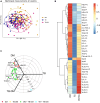
Diabetes mellitus (DM) increases tuberculosis (TB) susceptibility and worsens outcomes. Since inflammation and lipid metabolism are implicated in both diseases, we examined if combined TB and DM (TB-DM) increases inflammation or dyslipidaemia. In plasma from individuals with DM (n = 96), TB (n = 93), and TB-DM (n = 91), we measured 92 inflammatory proteins and 250 primarily lipid-related metabolites, repeating measurements after two months of TB treatment. Inflammation was primarily driven by TB, but higher in TB-DM. In TB-DM, the proteins osteoprotegerin (OPG), signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAMF1), adenosine deaminase (ADA), interleukin-10 receptor subunit beta (IL-10RB), and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFSR9) were differentially abundant, and IL-17A/C predicted treatment failure. Disease severity correlated with inflammation and dyslipidaemia. Inflammation decreased with TB treatment, both in TB and TB-DM. Dyslipidaemia was primarily driven by DM, but more pro-atherogenic in TB-DM, with elevated VLDL and apolipoprotein B (ApoB). Despite TB treatment, pro-atherogenicity persisted. Stronger inflammation and dyslipidaemia may account for worse disease outcomes in TB-DM and warrant further action to prevent cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Endocrinology; Health sciences; Immunology; Medical microbiology; Medical specialty; Medicine.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Podell B.K., Ackart D.F., Obregon-Henao A., Eck S.P., Henao-Tamayo M., Richardson M., Orme I.M., Ordway D.J., Basaraba R.J. Increased severity of tuberculosis in Guinea pigs with type 2 diabetes: a model of diabetes-tuberculosis comorbidity. Am. J. Pathol. 2014;184:1104–1118. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.12.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonio-Arques V., Caylà J.A., Real J., Moreno-Martinez A., Orcau À., Mauricio D., Mata-Cases M., Julve J., Navas Mendez E., Puig Treserra R., et al. Glycemic control and the risk of tuberculosis in patients with diabetes: A cohort study in a Mediterranean city. Front. Public Health. 2022;10 doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1017024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

