Sucroferric oxyhydroxide monotherapy for hyperphosphatemia in Indian chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis: A phase IV, single-arm, open-label study
- PMID: 40568335
- PMCID: PMC12001223
- DOI: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.100117
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide monotherapy for hyperphosphatemia in Indian chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis: A phase IV, single-arm, open-label study
Abstract
Background: Hyperphosphatemia (HP) is a common complication in an advanced stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with cardiovascular issues, metabolic bone abnormalities and worsening of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Most patients on dialysis require phosphate binders to control HP. Sucroferric oxyhydroxide (SO) (Dynulta™) is a calcium-free, polynuclear iron (III) based oral phosphate binder, for the treatment of HP. In this phase IV, open-label, single-arm, multi-center, 12-week, SOLO CKD study evaluated efficacy and safety of Dynulta™ in Indian CKD patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Aim: To investigate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of SO Chewable Tablet (Dynulta™) in patients with CKD on hemodialysis.
Methods: Hyperphosphatemic patients on hemodialysis and fulfilling eligibility criteria were included in the study for at least 12 weeks and received SO 1500 mg chewable tablet per day. The key endpoint was change in mean serum phosphorus levels after 12 weeks. Data were analysed using analysis of variance, Paired test, Wilcoxon test, and post-hoc comparisons, with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant, using Graph Pad software.
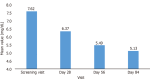
Results: A total of 114 patients were enrolled and 94 patients completed the study. The mean ± SD serum phosphorous level was reduced from 7.62 mg/dL ± 2.02 mg/dL at baseline to 5.13 mg/dL ± 1.88 mg/dL after 12 weeks of treatment. At each follow-up visit, the reduction in mean serum phosphorous levels was statistically significant (P value < 0.05) compared to baseline, confirming the efficacy of SO. A total of 33.33% of patients experienced adverse events (AEs). The most frequently reported AEs were pyrexia, nasopharyngitis and headache, which were considered unlikely to be related to the study drug treatment. No serious AEs was reported during the study period and no patients discontinued treatment due to AEs.
Conclusion: This first real-world study in Indian CKD patients on hemodialysis shows SO as a safe, and effective monotherapy for HP, though its small sample size limits generalizability.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Dynulta™; Hemodialysis; Hyperphosphatemia; Iron-based phosphate binder; Sucroferric oxyhydroxide.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Gaikwad A, Wangikar P, Suryawanshi S and Gajbe P are employees of Emcure Pharmaceuticals, India.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(46):1-233, i-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10460. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17083854
-
Bisphosphonates for breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Feb 15;(2):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub3. PMID: 16034900 Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Chen JB, Chiang SS, Chen HC, Obayashi S, Nagasawa M, Hexham JM, Balfour A, Junge G, Akiba T, Fukagawa M. Efficacy and safety of SBR759, a novel calcium-free, iron(III)-based phosphate binder, in Asian patients undergoing hemodialysis: A 12-week, randomized, open-label, dose-titration study versus sevelamer hydrochloride. Nephrology (Carlton) 2011;16:743–750. - PubMed
-
- Ruggiero B, Trillini M, Tartaglione L, Rotondi S, Perticucci E, Tripepi R, Aparicio C, Lecchi V, Perna A, Peraro F, Villa D, Ferrari S, Cannata A, Mazzaferro S, Mallamaci F, Zoccali C, Bellasi A, Cozzolino M, Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P, Kohan DE ANSWER Study Organization. Effects of Sevelamer Carbonate in Patients With CKD and Proteinuria: The ANSWER Randomized Trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:338–350. - PubMed
-
- Greig SL, Plosker GL. Sucroferric oxyhydroxide: a review in hyperphosphataemia in chronic kidney disease patients undergoing dialysis. Drugs. 2015;75:533–542. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous