Revisiting the effective connectivity within the distributed cortical network for face perception
- PMID: 40568430
- PMCID: PMC12172785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2021.100045
Revisiting the effective connectivity within the distributed cortical network for face perception
Abstract
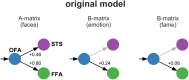
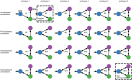
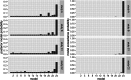
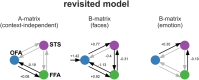
The classical core system of face perception consists of the occipital face area (OFA), fusiform face area (FFA), and posterior superior temporal sulcus (STS). The functional interaction within this network, more specifically the effective connectivity, was first described by Fairhall and Ishai (2007) using functional magnetic resonance imaging and dynamic causal modeling. They proposed that the core system is hierarchically organized; information is processed in a parallel and predominantly feed-forward fashion from the OFA to downstream regions such as the FFA and STS, with no lateral connectivity, i.e., no connectivity between the two downstream regions (FFA and STS). Over a decade later, we conducted a conceptual replication of their model using four different functional magnetic resonance imaging data sets. The effective connectivity within the core system was assessed with contemporary versions of dynamic causal modeling. The resulting model of the core system of face perception was densely interconnected. Using hierarchical linear modeling, we identified several significant forward, backward, and lateral connections in the core system of face perception across the data sets. Face perception increased the forward connectivity from the OFA to the FFA and OFA to the STS and increased the inhibitory backward connectivity from the FFA to the OFA, as well as the lateral connectivity between the FFA and STS. Emotion perception increased forward connectivity between the OFA and STS and decreased the lateral connectivity between the FFA and STS. Face familiarity did not significantly alter these connections. Our results revise the 2007 model of the core system of face perception. We discuss the potential meaning of the resulting model parameters and propose that our revised model is a suitable working model for further studies assessing the functional interaction within the core system of face perception. Our work further emphasizes the general importance of conceptual replications.
Keywords: Conceptual replication; Dynamic causal modeling; Emotion processing; Face perception; fMRI.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interhemispheric integration in the neural face perception network: Does stimulus location matter?Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 May 29;3:IMAG.a.17. doi: 10.1162/IMAG.a.17. eCollection 2025. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40800977 Free PMC article.
-
Does Augmenting Irradiated Autografts With Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in Patients With Bone Loss From a Malignant Tumor Achieve Union, Function, and Complication Rate Comparably to Patients Without Bone Loss and Augmentation When Reconstructing Intercalary Resections in the Lower Extremity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 26. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003599. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40569278
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Transformer-aided dynamic causal model for scalable estimation of effective connectivity.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Sep 23;2:imag-2-00290. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00290. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800338 Free PMC article.
-
Interhemispheric integration in the neural face perception network: Does stimulus location matter?Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 May 29;3:IMAG.a.17. doi: 10.1162/IMAG.a.17. eCollection 2025. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40800977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B.M., Walker S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Software. 2015;67 doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. - DOI
-
- Bedenbender J., Paulus F.M., Krach S., Pyka M., Sommer J., Krug A., Witt S.H., Rietschel M., Laneri D., Kircher T., Jansen A. Functional connectivity analyses in imaging genetics: considerations on methods and data interpretation. PLoS One. 2011;6 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Botvinik-Nezer R., Holzmeister F., Camerer C.F., Dreber A., Huber J., Johannesson M., Kirchler M., Iwanir R., Mumford J.A., Adcock R.A., Avesani P., Baczkowski B.M., Bajracharya A., Bakst L., Ball S., Barilari M., Bault N., Beaton D., Beitner J., Benoit R.G., Berkers R.M.W.J., Bhanji J.P., Biswal B.B., Bobadilla-Suarez S., Bortolini T., Bottenhorn K.L., Bowring A., Braem S., Brooks H.R., Brudner E.G., Calderon C.B., Camilleri J.A., Castrellon J.J., Cecchetti L., Cieslik E.C., Cole Z.J., Collignon O., Cox R.W., Cunningham W.A., Czoschke S., Dadi K., Davis C.P., Luca A., De Delgado M.R., Demetriou L., Dennison J.B., Di X., Dickie E.W., Dobryakova E., Donnat C.L., Dukart J., Duncan N.W., Durnez J., Eed A., Eickhoff S.B., Erhart A., Fontanesi L., Fricke G.M., Fu S., Galván A., Gau R., Genon S., Glatard T., Glerean E., Goeman J.J., Golowin S.A.E., González-García C., Gorgolewski K.J., Grady C.L., Green M.A., Guassi Moreira J.F., Guest O., Hakimi S., Hamilton J.P., Hancock R., Handjaras G., Harry B.B., Hawco C., Herholz P., Herman G., Heunis S., Hoffstaedter F., Hogeveen J., Holmes S., Hu C.P., Huettel S.A., Hughes M.E., Iacovella V., Iordan A.D., Isager P.M., Isik A.I., Jahn A., Johnson M.R., Johnstone T., Joseph M.J.E., Juliano A.C., Kable J.W., Kassinopoulos M., Koba C., Kong X.Z., Koscik T.R., Kucukboyaci N.E., Kuhl B.A., Kupek S., Laird A.R., Lamm C., Langner R., Lauharatanahirun N., Lee H., Lee S., Leemans A., Leo A., Lesage E., Li F., Li M.Y.C., Lim P.C., Lintz E.N., Liphardt S.W., Losecaat Vermeer A.B., Love B.C., Mack M.L., Malpica N., Marins T., Maumet C., McDonald K., McGuire J.T., Melero H., Méndez Leal A.S., Meyer B., Meyer K.N., Mihai G., Mitsis G.D., Moll J., Nielson D.M., Nilsonne G., Notter M.P., Olivetti E., Onicas A.I., Papale P., Patil K.R., Peelle J.E., Pérez A., Pischedda D., Poline J.B., Prystauka Y., Ray S., Reuter-Lorenz P.A., Reynolds R.C., Ricciardi E., Rieck J.R., Rodriguez-Thompson A.M., Romyn A., Salo T., Samanez-Larkin G.R., Sanz-Morales E., Schlichting M.L., Schultz D.H., Shen Q., Sheridan M.A., Silvers J.A., Skagerlund K., Smith A., Smith D.V., Sokol-Hessner P., Steinkamp S.R., Tashjian S.M., Thirion B., Thorp J.N., Tinghög G., Tisdall L., Tompson S.H., Toro-Serey C., Torre Tresols J.J., Tozzi L., Truong V., Turella L., van ‘t Veer A.E., Verguts T., Vettel J.M., Vijayarajah S., Vo K., Wall M.B., Weeda W.D., Weis S., White D.J., Wisniewski D., Xifra-Porxas A., Yearling E.A., Yoon S., Yuan R., Yuen K.S.L., Zhang L., Zhang X., Zosky J.E., Nichols T.E., Poldrack R.A., Schonberg T. Variability in the analysis of a single neuroimaging dataset by many teams. Nature. 2020;582:84–88. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2314-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
