Countering AI-generated misinformation with pre-emptive source discreditation and debunking
- PMID: 40568555
- PMCID: PMC12187399
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.242148
Countering AI-generated misinformation with pre-emptive source discreditation and debunking
Abstract
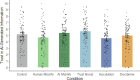
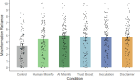
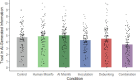
Despite widespread concerns over AI-generated misinformation, its impact on people's reasoning and the effectiveness of countermeasures remain unclear. This study examined whether a pre-emptive, source-focused inoculation-designed to lower trust in AI-generated information-could reduce its influence on reasoning. This approach was compared with a retroactive, content-focused debunking, as well as a simple disclaimer that AI-generated information may be misleading, as often seen on real-world platforms. Additionally, the extent to which trust in AI-generated information is malleable was also tested with an intervention designed to boost trust. Across two experiments (total N = 1223), a misleading AI-generated article influenced reasoning regardless of its alleged source (human or AI). In both experiments, the inoculation reduced general trust in AI-generated information, but did not significantly reduce the misleading article's specific influence on reasoning. The additional trust-boosting and disclaimer interventions used in Experiment 1 also had no impact. By contrast, debunking of misinformation in Experiment 2 effectively reduced its impact, although only a combination of inoculation and debunking eliminated misinformation influence entirely. Findings demonstrate that generative AI can be a persuasive source of misinformation, potentially requiring multiple countermeasures to negate its effects.
Keywords: continued influence effect; generative artificial intelligence; misinformation; source credibility.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Buchanan J, Hill S, Shapoval O. 2024. ChatGPT hallucinates non-existent citations: evidence from economics. Am. Econ. 69, 80–87. ( 10.1177/05694345231218454) - DOI
-
- Heppell F, Bakir ME, Bontcheva K. 2024. Lying blindly: bypassing ChatGPT’s safeguards to generate hard-to-detect disinformation claims at scale. arXiv. See http://arxiv.org/abs/2402.08467.
-
- Shukla AK, Tripathi S. 2024. AI-generated misinformation in the election year 2024: measures of European Union. Front. Polit. Sci 6, 1451601. ( 10.3389/fpos.2024.1451601) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

