Unraveling the immune mechanisms and therapeutic targets in lung adenosquamous transformation
- PMID: 40568576
- PMCID: PMC12188374
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1542526
Unraveling the immune mechanisms and therapeutic targets in lung adenosquamous transformation
Abstract
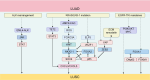
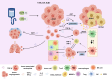
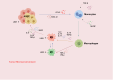
Adenocarcinoma-to-squamous cell carcinoma transformation (AST) induces drug resistance in patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), often resulting in unfavorable clinical outcomes. In recent years, it has been found that alterations in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) during adenosquamous carcinoma trans-differentiation also influence the efficacy of immunotherapy. Moreover, the aberrant expression and activation of several driver genes for AST lead to abnormal infiltration and function of immune cell by remodeling the cellular inflammatory phenotype. In this review, we will systematically present the changes in the TIME and molecular regulatory mechanisms during adenosquamous carcinoma differentiation, aiming to gain a better understand of the function of immune cells during this process and the potential value of combining immunotherapy to enhance the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Keywords: adenocarcinoma-to-squamous cell carcinoma transformation (AST); adenosquamous lung carcinoma (ASLC); tumor immune microenvironment (TIME); tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs); tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs).
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Yang, Wang, Lin, Zhang, Ni and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

