PA/MR imaging-guided precision phototherapy and efficacy evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma utilizing a targeted multifunctional nanoprobe
- PMID: 40568601
- PMCID: PMC12187729
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605048
PA/MR imaging-guided precision phototherapy and efficacy evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma utilizing a targeted multifunctional nanoprobe
Abstract
Introduction: Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) poses a significant challenge due to its poor prognosis, necessitating advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. The integration of near-infrared photoacoustic (PA) imaging with magnetic resonance (MR) imaging offers enhanced temporal and spatial resolution, exceptional optical contrast, and profound tissue penetration, positioning this combination as a highly promising technique for accurate and sensitive HCC diagnosis.
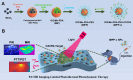
Methods: In this study, we developed a multifunctional and highly biocompatible nanoplatform, designated as ICG/Mn-PDA-PEG-CXCR4 (IMPP-c). This nanoplatform is designed to diagnose and treat early-stage HCC through PA/MR imaging-guided noninvasive photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT).
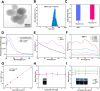
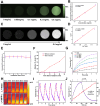
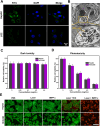
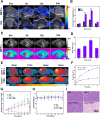
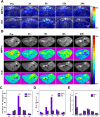
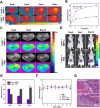
Results: Both in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated enhanced accumulation of IMPP-c nanoparticles (NPs) within HCC. Notably, the dual-modal PA/MR imaging facilitated by IMPP-c achieved high resolution and substantial deep tissue penetration, enabling precise localization of early orthotopic small hepatocellular carcinoma (SHCC) lesions. In vivo tumor phototherapy experiments, guided by PA/MR imaging, revealed that SHCC was completely eradicated through noninvasive PTT/PDT without recurrence. Additionally, the metabolism of IMPP-c NPs was observed in major organs throughout the treatment process, confirming its reliable biocompatibility.
Discussion: This study introduces a novel method for diagnosing and implementing non-invasive therapeutic interventions in early HCC using nanoparticle systems such as IMPP-c, paving the way for potential future clinical applications.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; magnetic resonance (MR) imaging; photoacoustic (PA) imaging; photodynamic therapy (PDT); photothermal therapy (PTT).
Copyright © 2025 Qi, Zhou, Liu, Shen, Yao, Tian, Liu, Cheng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted Multifunctional Nanoplatform for Imaging-Guided Precision Diagnosis and Photothermal/Photodynamic Therapy of Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Aug 30;17:3777-3792. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S377080. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36065288 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Targeted PLGA Nanospheres Enhance Therapeutic Effect of Lenvatinib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Aug 6;17(31):44922-44938. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c09045. Epub 2025 Jul 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40689931
-
Novel MR imaging nanoprobe for hepatocellular carcinoma detection based on manganese-zinc ferrite nanoparticles: in vitro and in vivo assessments.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jul;149(8):4939-4957. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04427-x. Epub 2022 Oct 29. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36309602 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 6;5(5):CD014798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35521901 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 2;9(9):CD013483. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013483.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36053210 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

