Biosynthesis of Biphenomycin-like Macrocyclic Peptides by Formation and Cross-Linking of Ortho-Tyrosines
- PMID: 40568902
- PMCID: PMC12257519
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c06044
Biosynthesis of Biphenomycin-like Macrocyclic Peptides by Formation and Cross-Linking of Ortho-Tyrosines
Abstract
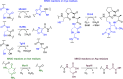
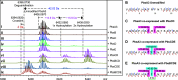
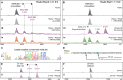
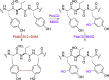
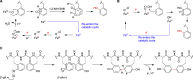
Ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides (RiPPs) are a growing class of natural products. Multinuclear nonheme iron-dependent oxidative enzymes (MNIOs, previously DUF692) are involved in a range of unprecedented biochemical reactions. Over 13,500 putative MNIO-encoding biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) have been identified by sequence similarity networks. In this study, we investigated a set of precursor peptides containing a conserved FHAFRF motif in MNIO-encoding BGCs. These BGCs contain genes encoding an MNIO, a RiPP recognition element-containing protein, an arginase, a hydroxylase, and a vitamin B12-dependent radical SAM enzyme (B12-rSAM). Using heterologous reconstitution of a representative BGC from Peribacillus simplex (pbs cluster) in E. coli, we demonstrated that the MNIO in conjunction with the partner protein catalyzes ortho-hydroxylation of each of the phenylalanine residues in the conserved FRF motif, the arginase forms an ornithine from the arginine, the ornithine residue is hydroxylated, and the B12-rSAM cross-links the ortho-Tyr side chains by a C-C linkage forming a macrocycle. A protease matures the RiPP to its final form. The elucidated structure shares close similarity to biphenomycins, a class of peptide antibiotics for which the biosynthetic pathway has not been characterized. Substrate scope studies suggest some tolerance of the MNIO and the B12-rSAM enzymes. This study expands the diverse array of posttranslational modifications catalyzed by MNIOs and B12-rSAM enzymes, deorphanizes biphenomycin biosynthesis, and provides a platform for the production of analogs from orthologous BGCs.
Figures



Update of
-
Biosynthesis of Macrocyclic Peptides by Formation and Crosslinking of ortho -Tyrosines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 8:2025.04.04.647296. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.04.647296. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Jul 9;147(27):23781-23796. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c06044. PMID: 40291698 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis of Macrocyclic Peptides by Formation and Crosslinking of ortho -Tyrosines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 8:2025.04.04.647296. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.04.647296. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Jul 9;147(27):23781-23796. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c06044. PMID: 40291698 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Multinuclear non-haem iron-dependent oxidative enzymes: landscape of their substrates, partner proteins and biosynthetic gene clusters.Microb Genom. 2025 Jul;11(7). doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001462. Microb Genom. 2025. PMID: 40742829
-
Exploring ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides through SPECO-based genome mining.Methods Enzymol. 2025;717:67-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2025.04.005. Epub 2025 May 24. Methods Enzymol. 2025. PMID: 40651835
-
Genome mining for natural products made by multinuclear iron-dependent oxidation enzymes (MNIOs).Methods Enzymol. 2025;717:89-117. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2025.01.060. Epub 2025 Feb 16. Methods Enzymol. 2025. PMID: 40651836 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Savile C. K., Janey J. M., Mundorff E. C., Moore J. C., Tam S., Jarvis W. R., Colbeck J. C., Krebber A., Fleitz F. J., Brands J., Devine P. N., Huisman G. W., Hughes G. J.. Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture. Science. 2010;329:305–309. doi: 10.1126/science.1188934. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

