Unique conformational dynamics and protein recognition of A-to-I hyper-edited dsRNA
- PMID: 40568935
- PMCID: PMC12199146
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf550
Unique conformational dynamics and protein recognition of A-to-I hyper-edited dsRNA
Abstract
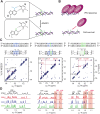
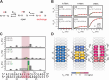
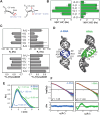
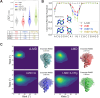
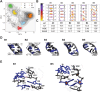
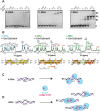
Adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) editing is a highly abundant modification of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays an important role in posttranscriptional gene regulation. Editing of multiple inosines by the ADAR1 enzyme leads to A-to-I hyper-editing of non-coding dsRNA, such as 3'UTRs, transposable elements, or foreign pathogenic RNAs, and is implicated in immune response and human diseases including cancer. The structural consequences of hyper-editing and its role in protein binding are poorly understood. Here, we combine solution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), biophysical methods such as small-angle X-ray scattering, and molecular dynamics simulations to study the sequence-dependent effects on conformation and dynamics of A-to-I hyper-editing for a 20-mer dsRNA and recognition of such RNAs by Endonuclease V. By comparing non-edited, single-edited, and hyper-edited dsRNA, we identify unique conformational features and extensive dynamics associated with hyper-editing, resulting in significantly increased base-pair opening. Hyper-edited dsRNA is more extended and adopts a highly dynamic ensemble of canonical and non-canonical conformations, which lead to preferential binding by Endonuclease V. Our integrated experimental and computational analysis identifies unique structural and dynamic features that are likely linked to specific protein recognition and the unique biological consequences of hyper-editing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

