Disentangling the effects of task difficulty and effort on flow experience
- PMID: 40569444
- PMCID: PMC12202627
- DOI: 10.1007/s00426-025-02128-x
Disentangling the effects of task difficulty and effort on flow experience
Abstract
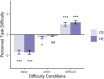
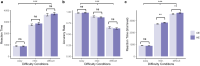
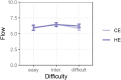
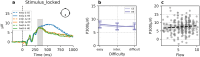
Flow, which is a rewarding state of full focus, typically arises when engaging in tasks with an optimal level of difficulty that is matched with a person's skill level. Meanwhile, optimal task difficulty usually comes with the greatest effort exertion. We propose that not only the difficulty level, but also the level of effort invested plays a role in the subjective feelings of flow. Using a visual discrimination task, we manipulated stimulus complexity and the expected probability of detecting a difference to induce and disentangle perceived task difficulty and effort exertion, respectively. Notably, perceived task difficulty increased proportionally with increasing stimulus complexity. Reaction time as an index of effort exertion, increased in challenging tasks with higher expectancy. Patterns of flow experience mirrored the observed shifts in effort exertion, suggesting a possible link between flow and effort. However, no parallel trend emerged in the physiological flow indicator, specifically the P300 amplitude. These findings highlight the intricate interplay between subjective experiences of task difficulty, exerted effort, and the subjective sense of being in 'flow'.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
P300 ERP System Utilizing Wireless Visual Stimulus Presentation Devices.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 7;25(12):3592. doi: 10.3390/s25123592. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573479 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
-
A common alteration in effort-based decision-making in apathy, anhedonia, and late circadian rhythm.Elife. 2025 Jun 16;13:RP96803. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96803. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40522113 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Reading aids for adults with low vision.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD003303. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003303.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakker, A. B., Oerlemans, W., Demerouti, E., Slot, B., B., & Ali, K. (2011). D. Flow and performance: A study among talented Dutch soccer players. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2011.02.003
-
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B. M., & Walker, S. C. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/JSS.V067.I01
-
- Biasutti, M., Tervaniemi, M., Addessi, A. R., Katahira, K., Yamazaki, Y., Yamaoka, C., Ozaki, H., Nakagawa, S., & Nagata, N. (2018). EEG correlates of the flow State: A combination of increased frontal Theta and moderate frontocentral alpha rhythm in the mental arithmetic task. Frontiers in Psychology, 1, 300. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00300 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bogdanov, M., Renault, H., LoParco, S., Weinberg, A., & Otto, A. R. (2022). Cognitive effort exertion enhances electrophysiological responses to rewarding outcomes. Cerebral Cortex, 32(19), 4255–4270. 10.1093/cercor/bhab480 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

