Severe Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in a US Naval Special Warfare Combatant Crewman
- PMID: 40569594
- PMCID: PMC12203286
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.17686
Severe Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in a US Naval Special Warfare Combatant Crewman
Abstract
Importance: Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a tauopathy mostly observed following a history of repeated impact-type head injury, usually from contact sports. The overwhelming majority of published, high-stage CTE cases are in older, former high-level contact sport athletes. CTE was infrequent in a large case series of brains donated by military service members, wherein it was most often of minimal severity, while being unanimously present in former contact sport participants.
Objective: To describe the neuropathological examination of a brain donated from a US Naval special warfare combatant crewman (SWCC) who had a 12-year career.
Design, setting, and participants: This case study of a whole brain specimen donated after death from a 44.9-year-old military donor with multiple deployments was conducted at a US biorepository dedicated to studies of brains donated from deceased military personnel. The detailed neuropathological examination included comprehensive molecular genetic testing.
Exposure: SWCC are trained to execute high-risk warfare and reconnaissance missions typically operating small, mobile, fast watercraft in numerous maritime environments, including operation in the high seas. In this context, SWCC sustain repetitive physical forces to the body from high-speed boat impacts with waves, which may number in the millions.
Main outcomes and measures: Postmortem diagnosis for CTE using the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NINDS-NIBIB) consensus criteria as well as the McKee staging system; molecular genetic assessment for neurodegenerative disease.
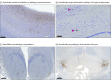
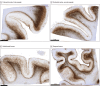
Results: The case specimen was from a male 44.9-year-old who served a 12.2-year SWCC career from ages 28.9 to 41.1 years. Following his last deployment, he experienced posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol misuse, migraines, and impaired cognition. He died by suicide. Neuropathological evaluation revealed severe CTE (high CTE according to NINDS-NIBIB consensus criteria; McKee Stage IV of IV), with extensive pathology involving numerous brain regions. Molecular genetic testing for neurodegenerative disease risk was negative.
Conclusions and relevance: In this neuropathological case study of a 44-year-old former SWCC, we found severe CTE. Given the severity of the pathology at a relatively young age, we consider that exposures of a SWCC career, including repetitive physical forces applied to the head from high-speed boat impacts with waves, may be sufficient to promote or otherwise contribute to CTE development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Roesch JR, Curley M, Hart B. Sudden impacts in Naval Special Warfare high-speed boats. Naval Surface Warfare Center report No. CSS/TR-94/38. September 1994. Accessed November 13, 2024. https://combatantcraftcrewman.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Impact-Repo...
-
- Kearns SD. Analysis and mitigation of mechanical shock effects on high speed planing boats. Massachusetts Institute of Technology graduate thesis. September 2001. Accessed November 13, 2024. https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/8235
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

