Fonsecazyma yulaniae sp. nov., a yeast species isolated from flowers
- PMID: 40569820
- PMCID: PMC12282027
- DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006830
Fonsecazyma yulaniae sp. nov., a yeast species isolated from flowers
Abstract
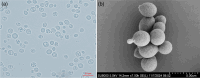
Two basidiomycete yeast strains, designated as 21S12 and 12S11, were isolated from the flowers of Yulania denudata collected from the Beijing Olympic Forest Park, PR China. Molecular phylogenetic analyses based on the D1/D2 domains of the large subunit rRNA gene and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region revealed that these strains represent a novel species within the genus Fonsecazyma. The new species, Fonsecazyma yulaniae sp. nov., is most closely related to Fonsecazyma mujuensis CBS 10308T, with sequence divergences of 4.3% (28 substitutions and 2 indels) in the D1/D2 domain and 8.4% (28 substitutions and 10 indels) in the ITS region. Phenotypically, F. yulaniae sp. nov. differs from F. mujuensis CBS 10308T in its ability to assimilate inulin and creatinine, as well as its inability to assimilate lactose and erythritol. Additionally, F. yulaniae sp. nov. can grow in a vitamin-free medium and in a medium supplemented with 50% glucose, conditions under which F. mujuensis cannot grow. The holotype of F. yulaniae sp. nov. is CGMCC2.5852T, and its taxonomic description has been registered in Fungal Names (FN572294) and in Mycobank (MBT10026390).
Keywords: Fonsecazyma; flower; novel species; phylogeny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Li A-H, Yuan F-X, Groenewald M, Bensch K, Yurkov AM, et al. Diversity and phylogeny of basidiomycetous yeasts from plant leaves and soil: proposal of two new orders, three new families, eight new genera and one hundred and seven new species. Stud Mycol. 2020;96:17–140. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2020.01.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

