Barriers to cataract surgeries as perceived by visually impaired 50 years and older cataract blind participants of Nepal survey for rapid assessment of avoidable blindness
- PMID: 40570012
- PMCID: PMC12200702
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312648
Barriers to cataract surgeries as perceived by visually impaired 50 years and older cataract blind participants of Nepal survey for rapid assessment of avoidable blindness
Abstract
Purpose: To identify the main barriers and determinants to cataract surgery as perceived by 50 years and older Nepali people with severe visual impairment & blind due to cataracts.
Methods: This was part of the Rapid Assessment for Avoidable Blindness (RAAB), held in all provinces of Nepal from 2018 to 2021. Cataract blindness was defined as a person having the best-corrected vision, < 6/60 in the better eye, and an unoperated cataract, which was the principal cause of visual disability. The participants were interviewed using a pretested questionnaire with seven known barriers. The demographic information was correlated with the barrier score.
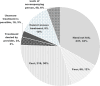
Results: We surveyed 718 cataract blind. Two-thirds of the participants were females. Four in ten were aged 50-59 years. The main barriers perceived were 'need is not felt' (237; 33%), cost associated with surgery (218; 30%), lack of access (93; 13%), fear of surgery (88; 12%), nobody to accompany (40; 6%), unaware of surgery (18; 3%), and treatment denied (24; 3%). The barriers were not significantly different in females than in males. (P = 0.85). The provincial variations of barriers were significant. (P < 0.001). High cost was a perceived barrier in all provinces except Gandaki. Access to treatment was a barrier in the Gandaki province (38%). One in four participants in the Madhesh and Bagmati provinces feared surgery. Nearly half of the cataract blind in the Madhesh and Lumbini province did not feel 'need for restoring vision'.
Conclusions: To improve cataract surgery uptake, identified barriers, like lack of awareness, low visual need, and high cost must be addressed. The strategies could be devised according to provincial barriers but similar to both genders and all 50 years and older cataract blind. Offering low-cost cataract surgery, financial assistance and health promotion to improve awareness and remove fear were recommended.
Copyright: © 2025 Shah et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgery for cataracts in people with age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 16;2(2):CD006757. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006757.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28206671 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve access to cataract surgical services and their impact on equity in low- and middle-income countries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 9;11(11):CD011307. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011307.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29119547 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of macular oedema after cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 1;11(11):CD006683. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006683.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27801522 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus corticosteroids for controlling inflammation after uncomplicated cataract surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 3;7(7):CD010516. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010516.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28670710 Free PMC article.
-
Community screening for visual impairment in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 20;2(2):CD001054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001054.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29460275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study, GBD 2019 Blindness and Vision Impairment Collaborators. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by cataract: a meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye (Lond). 2024;38(11):2156–72. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-02961-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical