Cost-utility of aripiprazole once-monthly versus paliperidone palmitate once-monthly injectable for schizophrenia in China
- PMID: 40570029
- PMCID: PMC12200646
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317393
Cost-utility of aripiprazole once-monthly versus paliperidone palmitate once-monthly injectable for schizophrenia in China
Abstract
Objectives: From the perspective of Chinese healthcare system, this study compared the cost-utility of aripiprazole once-monthly (AOM) and paliperidone palmitate once-monthly injectable (PP1M) in the treatment of adult patients with schizophrenia in China.
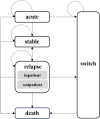
Methods: A 5-state Markov model was developed to evaluate the cost-utility of 10 years of long-acting injections (LAI) treatment for schizophrenia. The long-term costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were estimated, with the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) as the primary outcome. The annual discount rate was set at 5%. A cost-effectiveness threshold (CET) of 0.51 times China's 2023 gross domestic product (GDP) (US$ 6,394.536) was used to judge the economics of intervention.
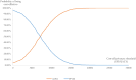
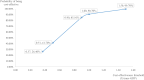
Results: The current price of AOM in China is relatively high (US$418.140). To assess its cost-effectiveness in the context of potential price negotiations with China Healthcare Security Administration (CHS) for inclusion in the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL), we simulated a 40% price reduction (US$257.619). At a CET of 0.51 times GDP per capita (US$6,394.536), the base-case analysis showed that the incremental costs of AOM relative to PP1M after 10 years of treatment were US$1,926.373 with an incremental gain of 0.306 QALYs. The ICER for AOM was US$6,285.303 per QALY, which is below the CET, indicating that AOM is cost-effective. One-way sensitivity analysis identified AOM's drug cost as the parameter with the greatest impact on results. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis revealed that with a 40% price reduction, the probability of AOM being cost-effective is only 41.70%. However, with a 60% price reduction, AOM became dominantly cost-effective, with the probability increasing to 100%. When the CET was relaxed to 0.90 times GDP per capita (US$11,284.476), the probability of cost-effectiveness for AOM after a 40% price reduction rose to 85.10%. Scenario analyses conducted over a time horizon extending from 10 to 30 years showed that the ICER decreased significantly with longer follow-up, gradually approaching the 0.51GDP threshold and remaining below the 0.90 GDP threshold throughout the analysis.
Conclusions: The cost-effectiveness of AOM relative to PP1M is highly influenced by its price and the CET. Healthcare decision makers or clinical users need to balance innovation incentives and accessibility.
Copyright: © 2025 An et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of TV-46000 and Second-Generation Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics for Schizophrenia: A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Adv Ther. 2025 Sep;42(9):4188-4209. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03274-9. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40668497 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(47):iii-iv, ix-248. doi: 10.3310/hta11470. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999842
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Systematic review and cost-effectiveness evaluation of 'pill-in-the-pocket' strategy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation compared to episodic in-hospital treatment or continuous antiarrhythmic drug therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jun;14(31):iii-iv, 1-75. doi: 10.3310/hta14310. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20569652
References
-
- Citrome L, Kamat SA, Sapin C, Baker RA, Eramo A, Ortendahl J, et al. Cost-effectiveness of aripiprazole once-monthly compared with paliperidone palmitate once-monthly injectable for the treatment of schizophrenia in the United States. J Med Econ. 2014;17(8):567–76. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2014.917089 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wufang Z, Ning M, Xun W, Xiamin W, Miaomiao Z, Runzi C. Management and services for psychosis in the People′s Republic of China in 2020. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry. 2022;5(22).
-
- Haoming Y, Peidong M, Hongyun D. Influencing factors and preventive strategies of drug compliance and recurrence in patients with schizophrenia. China Journal of Health Psychology. 2021;29(06):816–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

