Understanding carboxysomes to enhance carbon fixation in crops
- PMID: 40570186
- PMCID: PMC12312397
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20253072
Understanding carboxysomes to enhance carbon fixation in crops
Abstract
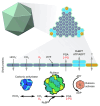
Carboxysomes are bacterial microcompartments that enhance photosynthetic CO2 fixation by encapsulating ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) within a high-CO2 environment. Their modular, self-assembling nature makes them attractive for synthetic biology applications, particularly their transplantation alongside functional bicarbonate (HCO3-) transporters into plant chloroplasts to achieve improved photosynthetic efficiency. Recent advances have deepened our understanding of carboxysome biogenesis, Rubisco organisation and shell function. However, key questions remain, including the precise shell mechanistic action, which is critical for functional integration into new hosts. Addressing these questions, as well as identifying suitable bicarbonate transporters and fine-tuning expression levels, will be essential to utilising carboxysomes and the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating mechanism for enhanced photosynthetic efficiency in crops.
Keywords: Rubisco; carbon fixation; cyanobacteria; photosynthesis; synthetic biology.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

