Prospective Multicenter Study Evaluating a Combined Circulating Tumor DNA and Circulating Tumor RNA Liquid Biopsy in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (LIQUIK)
- PMID: 40570258
- PMCID: PMC12203978
- DOI: 10.1200/PO-25-00181
Prospective Multicenter Study Evaluating a Combined Circulating Tumor DNA and Circulating Tumor RNA Liquid Biopsy in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (LIQUIK)
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the performance of a circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and circulating tumor RNA (ctRNA) liquid biopsy, LiquidHALLMARK (LHM), compared with tissue next-generation sequencing (NGS) and Guardant360 CDx (G360 ctDNA) liquid biopsy for biomarker detection in metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer.
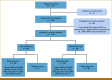
Patients and methods: This multicenter, prospective study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04703153) enrolled patients across the United States and Singapore. Patients were tested with tissue NGS, LHM, and G360 ctDNA. The primary objective was noninferiority of LHM ctDNA to tissue NGS and G360 ctDNA. Secondary analyses included turnaround time (TAT), overall response rate (ORR), and progression-free survival (PFS), with exploratory analysis of the clinical utility of ctRNA.
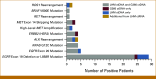
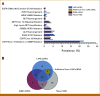
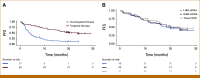
Results: LHM ctDNA (48.2%) detected 11.4% fewer biomarker-positive patients than tissue NGS (59.6%) and did not meet noninferiority criteria. Compared with tissue NGS, LHM ctDNA and G360 ctDNA were concordant in 72.1% and 66.1% of patients, establishing noninferiority of LHM ctDNA to G360 ctDNA (P = .002). TAT was shorter for LHM ctDNA than for tissue NGS (mean 9.7 v 21.7 days; P < .001). ORR/PFS was similar in patients receiving targeted therapy based on all three assays. Addition of ctRNA increased the diagnostic yield of tissue NGS-confirmed gene rearrangements by 28.6% relative to LHM ctDNA and all actionable biomarkers by 15.6% relative to G360 ctDNA. LHM ctDNA and ctRNA (51/68) detected 8.8% more biomarker-positive patients than G360 ctDNA (45/68), demonstrating superiority of LHM ctDNA and ctRNA (P = .001).
Conclusion: LHM ctDNA is noninferior to G360 ctDNA, but not tissue NGS. Treatment outcomes based on liquid biopsy are comparable with those based on tissue NGS. Incorporation of ctRNA into LHM ctDNA improves the diagnostic yield of actionable, tissue NGS-confirmed gene rearrangements.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detecting actionable mutations from matched plasma-based versus tissue next-generation sequencing in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective single centre analysis on site.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 6;44(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03480-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40765058 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Testing Among Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the United States: Predictive Modeling Using Machine Learning Methods.JMIR Cancer. 2025 Jun 11;11:e64399. doi: 10.2196/64399. JMIR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40497643 Free PMC article.
-
LIBELULE: A Randomized Phase III Study to Evaluate the Clinical Relevance of Early Liquid Biopsy in Patients With Suspicious Metastatic Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2025 Apr;20(4):437-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.12.011. Epub 2024 Dec 16. J Thorac Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39694415 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Utility of ctDNA Analysis in Lung Cancer-A Review.Adv Respir Med. 2025 Jun 12;93(3):17. doi: 10.3390/arm93030017. Adv Respir Med. 2025. PMID: 40558116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postoperative Circulating Tumour DNA in Predicting Recurrence of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2025 Aug;44:103892. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2025.103892. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2025. PMID: 40614309
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. : Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 74:229-263, 2024 - PubMed
-
- Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Aisner DL, et al. : Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med 142:321-346, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al. : Non–small cell lung cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 20:497-530, 2022 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

