Efficacy of Solifenacin, Mirabegron, and Combination Therapy in Children With Daytime Urinary Incontinence (BeDry): Protocol for a Randomized Single-Blinded Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40570329
- PMCID: PMC12246757
- DOI: 10.2196/63588
Efficacy of Solifenacin, Mirabegron, and Combination Therapy in Children With Daytime Urinary Incontinence (BeDry): Protocol for a Randomized Single-Blinded Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: According to International Children's Continence Society, the first-line treatment of children with daytime urinary incontinence is standard urotherapy, eventually followed by pharmacotherapy of anticholinergics. The effect of medical treatment is sparsely investigated and has been investigated primarily in nonrandomized trials.
Objective: The primary objective of this trial is to evaluate if (1) combination therapy of solifenacin and mirabegron in low doses is superior to monotherapy of solifenacin in high dose and if (2) combination therapy of mirabegron and solifenacin in low doses is superior to monotherapy of mirabegron in high dose in the treatment of daytime urinary incontinence among children aged 5-14 years who are noncomplete responders to monotherapy of solifenacin in low dose or monotherapy of mirabegron in low dose. The secondary objective is to evaluate the treatment response of combination therapy of solifenacin and mirabegron in low doses, monotherapy in high doses, and monotherapy in low doses as supplementary comparisons. Additionally, the secondary objective is to evaluate the side effects, safety, and tolerability of the medical treatment as well as the effect of the treatment on the well-being and quality of life.
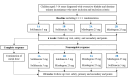
Methods: Children aged 5-14 years diagnosed with daytime urinary incontinence refractory to standard urotherapy will be randomized 1:1:1:1 to 4 treatment groups. Initially, 2 groups will receive solifenacin 5 mg and 2 groups will receive mirabegron 25 mg. After 6 weeks, noncomplete responders will receive add-on treatments according to their primary randomization group. Group 1A will receive solifenacin 5 mg and add-on solifenacin 5 mg, group 1B will receive solifenacin 5 mg and add-on mirabegron 25 mg, group 2A will receive mirabegron 25 mg and add-on mirabegron 25 mg, and group 2B will receive mirabegron 25 mg and add-on solifenacin 5 mg. The total treatment period will be 18 weeks. The primary end point measure is treatment response assessed by change from visit 2 to the end of the study, according to the number of wet days per 7 days by DryPie.
Results: The BeDry study was approved by Clinical Trials in the European Union on June 12, 2024. Recruitment began on June 27, 2024, and will continue until 236 patients are included, which is expected to occur by September 2026. As of April 2025, 75 participants are included.
Conclusions: This trial has the potential to optimize the medical treatment of children with daytime urinary incontinence, shorten the treatment period, diminish the side effects, and minimize unnecessary medical expenses.
Trial registration: Clinical Trials in the European Union EUCT 2023-510187-13-00; https://tinyurl.com/2hva7ph8; ClinicalTrials.gov NCT06551246; https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06551246.
International registered report identifier (irrid): PRR1-10.2196/63588.
Keywords: Denmark; children; mirabegron; monotherapy; multicenter; outpatient clinics; overactive bladder; pediatric; pharmacotherapy; protocol; randomized controlled trial; solifenacin; teenager; urinary incontinence; urotherapy.
©Ann-Kristine Mandøe Svendsen, Søren Hagstrøm, Kristina Thorsteinsson, Jason Van Batavia, Konstantinos Kamperis, Anne Estrup Olesen, Luise Borch. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (https://www.researchprotocols.org), 26.06.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strategy for Withdrawal of Pharmacological Treatment for Urinary Incontinence in Children (StayDry): Protocol for an Open-Label Prospective Randomized Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Jul 9;14:e63226. doi: 10.2196/63226. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40633093 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Mirabegron Compared to Solifenacin in Treatment of Non-neurogenic Overactive Bladder in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int Braz J Urol. 2025 Mar-Apr;51(2):e20240425. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2024.0425. Int Braz J Urol. 2025. PMID: 39913092 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of efficacy of mirabegron, solifenacin, tadalafil 5 mg and combination therapy in female patients with overactive bladder: a double blinded multicenter prospective placebo-controlled trial.Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun;77(3):383-395. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.25.06129-4. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40265720 Clinical Trial.
-
Which anticholinergic drug for overactive bladder symptoms in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD005429. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005429.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258963
-
[Efficacy and safety of available therapies in the management of idiopathic overactive bladder: A systematic review of the literature].Prog Urol. 2017 Mar;27(4):203-228. doi: 10.1016/j.purol.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Prog Urol. 2017. PMID: 28228331 French.
References
-
- Chang S, Van Laecke E, Bauer SB, von Gontard A, Bagli D, Bower WF, Renson C, Kawauchi A, Yang SS. Treatment of daytime urinary incontinence: A standardization document from the International Children's Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Jan;36(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/nau.22911. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Warner T, Baandrup U, Jacobsen R, Bøggild H, Aunsholt Østergaard P S, Hagstrøm S. Prevalence of nocturia and fecal and urinary incontinence and the association to childhood obesity: a study of 6803 Danish school children. J Pediatr Urol. 2019 May;15(3):225.e1–225.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2019.02.004.S1477-5131(19)30042-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous