Poly(lactic- co-glycolic acid) Microspheres Encapsulating a Viral-Binding Protein, PmRab7, for Preventing White Spot Syndrome Virus in Shrimp
- PMID: 40570360
- PMCID: PMC12264765
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00928
Poly(lactic- co-glycolic acid) Microspheres Encapsulating a Viral-Binding Protein, PmRab7, for Preventing White Spot Syndrome Virus in Shrimp
Abstract
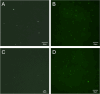
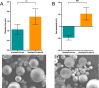
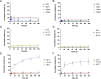
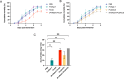
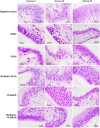
White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) is one of the most devastating pathogens affecting shrimp. Within a short time, it leads to a hundred percent mortality rate, which causes substantial economic losses. PmRab7 has been reported to bind to the envelope protein of WSSV, VP28, resulting in a reduction of viral replication. In order to apply PmRab7 in shrimp feed, the development of delivery systems is crucial. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) is a biodegradable polymer extensively studied for drug delivery in the form of nanoparticles or microspheres (MSs). Despite its potential, PLGA has not been previously reported for antiviral use in shrimp. This study is the first to demonstrate the potential use of PLGA and chitosan-coated PLGA (PLGA/CS) MSs for the delivery of PmRab7 in shrimp. Both PLGA and PLGA/CS were optimized and characterized to allow for a sustained release of encapsulated PmRab7. Initial in vitro and in vivo evaluations demonstrated that both MSs are safe for use in shrimp, can sustain the release of PmRab7, and enhance its antiviral activity as shown by a decrease in the mortality rate in shrimp. The development of these MSs has the potential to significantly enhance disease control in shrimp aquaculture, leading to more effective and sustainable practices that will ultimately bolster the industry's growth and long-term stability.
Keywords: PLGA; PmRab7; chitosan; microspheres; white spot syndrome virus.
Figures


References
-
- Kumkoon T., Chunhavacharatorn P., Manohong P., Nirmal N., Benjakul S., Katewongsa K.. Anti-Cancer Activity of Ethanolic Extract from ‘Bao’ Mango (Mangifera indica) Peel and Its Nanoencapsulation Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines. ChemNanoMat. 2024;10(6):e202300530. doi: 10.1002/cnma.202300530. - DOI
-
- Mekseriwattana W., Phungsom A., Sawasdee K., Wongwienkham P., Kuhakarn C., Chaiyen P., Katewongsa K. P.. Dual Functions of Riboflavin-functionalized Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Drug Delivery Efficiency and Photodynamic Therapy in Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021;97(6):1548–1557. doi: 10.1111/php.13464. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Payomhom P., Panyain N., Sakonsinsiri C., Wongtrakoongate P., Lertsuwan K., Pissuwan D., Katewongsa K. P.. Chitosan-Coated Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Loaded with Ursolic Acid for Breast Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024;7(5):5383–5395. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c06161. - DOI
-
- Sawasdee K., Sucharitakul J., Dhammaraj T., Niamsiri N., Chaiyen P., Prapainop K.. Encapsulation of the reductase component of p -hydroxyphenylacetate hydroxylase in poly(lactide-co -glycolide) nanoparticles by three different emulsification techniques. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018;12(4):423–428. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maphanao P., Phothikul Y., Choodet C., Puangmali T., Katewongsa K., Pinlaor S., Thanan R., Yordpratum U., Sakonsinsiri C.. Development and in vitro evaluation of ursolic acid-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles in cholangiocarcinoma. RSC Adv. 2024;14(34):24828–24837. doi: 10.1039/D4RA03637A. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
