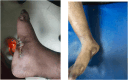
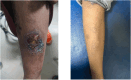
Management of Epidermolysis Bullosa through Ayurveda- a case report of two siblings
- PMID: 40570575
- PMCID: PMC12246705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2025.101149
Management of Epidermolysis Bullosa through Ayurveda- a case report of two siblings
Abstract
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of inherited rare skin disorders that causes the skin to become fragile and blister easily due to minor trauma or friction. Blisters can appear anywhere on the body. There are limitations in treating this disease in the conventional system of medicine. This paper elaborates on the case of two siblings who presented with blisters all over the body with itching, discharge, difficulty in walking, and disfigurement of fingers, toes, and feet. Based on Ayurvedic clinical assessment, the condition was diagnosed as Kapha-pitta dominant Tridoshaja Visphota. They were treated through Ayurveda on the line of Visphota (a type of Kushtha/skin disorder) with the use of Dipana (digestion and metabolism-enhancing), Pachana (enhancing digestion), and Mridu Shodhana (mild bio-cleansing) medicines. Both patients have shown improvement with a reduction in EBDASI (Epidermolysis bullosa disease activity and scaring index) from 174 to 45 and 176 to 39, respectively, in the first and second sibling with 4 months of ayurvedic medication. No relapse was seen in both patients during the next one year. The case study is unique as EB is a genetic disorder with limitations in its management in the conventional system of medicine. Moreover, the authors could not find any published case of EB managed through Ayurveda treatment. Thus, it opens new areas of research in the management of EB through traditional systems of medicine like Ayurveda.
Keywords: Ayurveda; Blister; Bullous diseases; Epidermolysis bullosa; Panchakarma; Visphota.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest for the submitted manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex.1998 Oct 7 [updated 2022 Aug 4]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 1998 Oct 7 [updated 2022 Aug 4]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301543 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Psychometric Properties of the Instrument for Scoring Clinical Outcomes of Research for Epidermolysis Bullosa patient score (iscorEB-p): a patient-reported outcome measure.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):75-81. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae019. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38261404
-
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa.2006 Aug 21 [updated 2025 Aug 7]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2006 Aug 21 [updated 2025 Aug 7]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301481 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is associated with glycolytically active GATA3+ T helper 2 cells which may contribute to pruritus in lesional skin.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):252-260. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae110. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38477474
References
-
- Baardman R., Yenamandra V.K., Duipmans J.C., Pasmooij A.M.G., Jonkman M.F., van den Akker P.C., et al. Novel insights into the epidemiology of epidermolysis bullosa (EB) from the Dutch EB Registry: EB more common than previously assumed? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35(4):995–1006. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uitto J., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Christiano A.M., McGrath J.A., Has C., South A.P., Kopelan B., Robinson E.C. Progress toward treatment and cure of epidermolysis bullosa: summary of the DEBRA international research symposium EB2015. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(2):352–358. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2015.10.050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources