TCF3 and ID3 Regulate TSPAN32 Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma
- PMID: 40572059
- PMCID: PMC12202839
- DOI: 10.1111/sji.70040
TCF3 and ID3 Regulate TSPAN32 Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma
Abstract
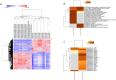
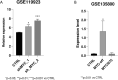
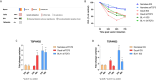
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma characterised by chromosomal translocations involving the MYC gene, leading to its overexpression and driving uncontrolled proliferation. BL is categorised into endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-associated subtypes, each with distinct clinical and epidemiological features. TSPAN32, a member of the tetraspanin family, plays a key role in B cell development and immune regulation. In this study, we investigated the regulation of TSPAN32 expression in BL subtypes. Our results show that TSPAN32 expression is significantly downregulated in endemic, sporadic, and HIV-associated BL. Notably, this downregulation is independent of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, as no significant differences in TSPAN32 expression were observed between EBV-positive and EBV-negative BL clones. Functional studies revealed that overexpression of a wild-type ID3 gene, a known repressor of TCF3, and knockdown of TCF3, both led to a significant upregulation of TSPAN32, particularly in BL41 and Daudi cells, which harbour ID3 mutations. Supporting this, ChIP-seq analysis identified TCF3 binding peaks on the TSPAN32 gene, providing mechanistic evidence of its regulation by TCF3. These findings shed light on the complex transcriptional network regulating TSPAN32 and its dysregulation in BL. Overall, our study suggests that TSPAN32 may serve as both a biomarker and a potential therapeutic target for this disease.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma; TSPAN32; tetraspanins.
© 2025 The Author(s). Scandinavian Journal of Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Scandinavian Foundation for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comprehensive analysis of transcription factors identified TCF3 as a prognostic target for glioma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 13;15(1):25314. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09924-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40653505 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-29 silencing modulates the expression of target genes related to proliferation, apoptosis and methylation in Burkitt lymphoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Mar;144(3):483-497. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2575-3. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29318382 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-320a expression shows correlation with viral load in EBV-negative Burkitt lymphoma samples.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2025 Jul 3:1-18. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2025.2527141. Online ahead of print. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40611431
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 13;9(9):CD013365. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013365.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34515338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graham B. S. and Lynch D. T., Burkitt Lymphoma (StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, 2024). - PubMed
-
- Harris N. L., Jaffe E. S., Diebold J., et al., “The World Health Organization Classification of Neoplastic Diseases of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues: Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee Meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November, 1997,” Annals of Oncology 10, no. 12 (1999): 1419–1432, 10.1023/A:1008375931236. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

