Chlorophyllin-Mediated Photodynamic Inactivation: Dosage and Time Dependency in the Inhibition of Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 40572076
- PMCID: PMC12195115
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13061189
Chlorophyllin-Mediated Photodynamic Inactivation: Dosage and Time Dependency in the Inhibition of Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
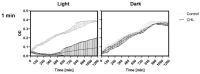
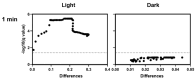
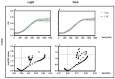
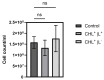
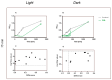
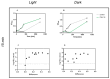
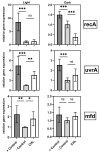
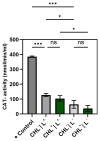
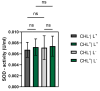
Photodynamic inactivation of bacteria offers a promising alternative to counteract the trend towards the development of resistance, which, if left uncontrolled, will lead to the death of 10 million people per year by 2050. Its advantage over antibiotics is the site-specific mode of action due to the photosensitizer (PS) and the low risk of developing resistance. This is primarily prevented by the damage of the bacteria, which also destroy internal structures such as nucleic acid, proteins, and lipids. A promising and still little-researched PS is chlorophyllin (CHL), a chlorophyll derivative. This study investigated its mode of action on Bacillus subtilis growth using optical density (OD) measurements. It was shown that the PS is highly effective even at low concentrations and short irradiation durations. Here, 1 mg/L and an irradiation duration of 1 min were sufficient to inhibit the growth of the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis for several hours.
Keywords: antibiotic alternatives; chlorophyllin; photodynamic inactivation (PDI); photodynamic therapy (PDT); photosensitizer.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Michael Lebert is engaged with the company Space Biology Unlimited, SAS. There is no conflict of interest regarding this MS. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- O’Neill J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. Volume 2014. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; London, UK: 2014. pp. 1–16.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

