Comparative Analysis of Nano-Bactericides and Thiodiazole-Copper on Tomato Rhizosphere Microbiome
- PMID: 40572215
- PMCID: PMC12195157
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13061327
Comparative Analysis of Nano-Bactericides and Thiodiazole-Copper on Tomato Rhizosphere Microbiome
Abstract
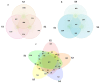
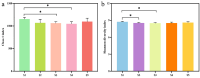
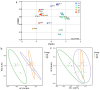
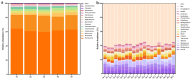
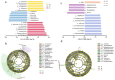
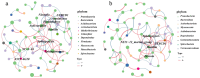
Vegetable crops such as tomato are highly susceptible to various pathogens. Nanoparticles (NPs) are emerging as effective nano-bactericides for managing plant pathogens. Communities of rhizosphere bacteria are essential for plant physiological health and also serve as a critical factor in evaluating the environmental compatibility of NPs. We evaluated the effects of a nano-bactericide (Cu-Ag nanoparticles) and a commercial bactericide (thiodiazole-copper) on the rhizosphere microbiome of tomato. The results show that low and high doses of the two bactericides induced alterations in the bacterial community structure to differing extents. Cu-Ag nanoparticles increased the relative abundance of potentially beneficial bacteria, including Bacteroidota, Gemmatimonadota, Acidobacteriota, and Actinobacteriota. Functional prediction revealed that Cu-Ag nanoparticles may affect the metabolic pathways of tomato root rhizosphere microorganisms and regulate the lacI/galR family, which controls virulence factors and bacterial metabolism. This study provides insight into the influence of metal nanoparticles on plant rhizosphere microbiomes and may lay a foundation for the application of nano-bactericides for the environmentally friendly control of plant diseases.
Keywords: microbial community; nano-bactericide; nanoparticles; rhizosphere; tomato.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cu-Ag nanoparticles positively modulating the endophytic bacterial community in tomato roots affected by bacterial wilt.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 16;16:1579517. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1579517. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40740341 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of saffron-grape intercropping on saffron flower number and rhizosphere microbial community.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Dec 30;24(1):551. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03716-4. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39736513 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics Reveals the Effect of Root Rot on Polygonati Rhizome and Identifies Pathogens and Biocontrol Strain.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0238521. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02385-21. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35225655 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis: a novel therapeutic mechanism in lung cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jun 24;25(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03864-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40555995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rathore A.C., Mehta H., Jayaprakash J., Singh C., Gupta A.K., Kumar P., Islam S., Kar S.K., Patra S., Chand L., et al. Modified plant architecture integrated with liquid fertilizers improves fruit productivity and quality of tomato in North West Himalaya, India. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:18664. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98209-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

