Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of Pathogenic Aeromonas caviae from Diseased Macrobrachium rosenbergii
- PMID: 40572230
- PMCID: PMC12195509
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13061343
Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of Pathogenic Aeromonas caviae from Diseased Macrobrachium rosenbergii
Abstract
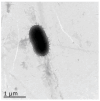
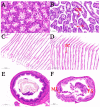
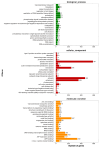
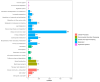
In recent years, viral and bacterial diseases have posed serious challenges to the sustainable development of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (giant freshwater prawn) aquaculture, resulting in considerable economic losses across China. Among the bacterial pathogens, Aeromonas caviae has emerged as a notable opportunistic agent capable of causing large-scale mortality in various aquatic species. In this study, a highly virulent strain of A. caviae (designated GMRS4) was isolated from diseased M. rosenbergii exhibiting mass mortality in Yangzhou, Jiangsu Province. The isolate, a Gram-negative bacillus, was identified as the causative agent based on morphological, molecular, and histopathological analyses. Pathogenicity was confirmed through experimental infection, with the strain displaying marked virulence, evidenced by an LD50 of 1.91 × 106 CFU/mL at 96 h. Whole-genome sequencing of GMRS4 revealed 4078 coding sequences, including a suite of virulence-associated genes encoding extracellular enzymes (DNase, hemolysin, caseinase, and lecithinase) and toxins (serine protease, elastase, and flagellin). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing indicated resistance to several antibiotics, particularly those in the penicillin and sulfonamide classes, while maintaining sensitivity to quinolones. Genomic analysis further revealed multiple antibiotic resistance genes and virulence genes, offering insights into the pathogenic mechanisms and resistance profile of the strain. This study underscores the threat posed by A. caviae to freshwater prawn aquaculture and provides a genetic basis for developing targeted disease management strategies.
Keywords: Aeromonas caviae; Macrobrachium rosenbergii; complete genome; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synergistic of Lactobacillus plantarum L20 and Sargassum polycystum hydrolysate enhances growth, immunity, and disease resistance against necrotizing hepatopancreatitis-like diseases-causing Aeromonas veronii in giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii).Dev Comp Immunol. 2025 Aug;169:105412. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2025.105412. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Dev Comp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40639760
-
Emergence of highly virulent Aeromonas dhakensis in channel catfish aquaculture: Genomic insights into pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2525933. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2525933. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40601807 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and virulence gene profiles of a pathogenic Lactococcus garvieae isolated from diseased Macrobrachium rosenbergii.Braz J Microbiol. 2025 Jun;56(2):1357-1370. doi: 10.1007/s42770-025-01653-6. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Braz J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40100617
-
Prophylactic antibiotics for adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 15;1(1):CD013198. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013198.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33448349 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics for exacerbations of asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 25;6(6):CD002741. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002741.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29938789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chavanne H., Janssen K., Hofherr J., Contini F., Haffray P., Consortium A., Komen H., Nielsen E.E., Bargelloni L. A comprehensive survey on selective breeding programs and seed market in the European aquaculture fish industry. Aquac. Int. 2016;24:1287–1307. doi: 10.1007/s10499-016-9985-0. - DOI
-
- Regan T., Bean T.P., Ellis T., Davie A., Carboni S., Migaud H., Houston R.D. Genetic improvement technologies to support the sustainable growth of UK aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2021;13:1958–1985. doi: 10.1111/raq.12553. - DOI
-
- Li J., Xu S., Cai Y., Jiang Y., Chen H., Lin L., Lv X. The effects of net-chasing training on survival and growth are related to stocking density in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture. 2022;561:738621. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738621. - DOI
-
- Tan K., Wang W. The early life culture and gonadal development of giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii: A review. Aquaculture. 2022;559:738357. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738357. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

