Nasal Colonizers from Sows in the Federal District of Brazil Showed a Diverse Phenotypic Resistance Profile
- PMID: 40572242
- PMCID: PMC12196429
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13061354
Nasal Colonizers from Sows in the Federal District of Brazil Showed a Diverse Phenotypic Resistance Profile
Abstract
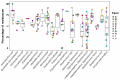
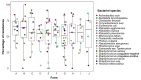
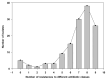
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major public health concern influenced by antimicrobial use (AMU) in animal production systems. In swine, metaphylactic treatments may contribute to the emergence and dissemination of resistance genes. In this study, we isolated bacteria from the nasal cavities of 50 sows across 10 farms in the Federal District, Brazil. A total of 132 bacterial isolates were obtained and tested for phenotypic resistance to 23 antimicrobials using the disk diffusion method. Resistance was detected against all tested antimicrobials, with an overall resistance rate of 55.6% (1605/2888 tests). The highest resistance rates were observed for bacitracin (92.4%) and penicillin (79.2%), while lower resistance rates were found for aminoglycosides. Most isolates exhibited multidrug resistance to 7-9 classes of antimicrobials, including strains of Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella-all of which are relevant in the context of One Health. Actinobacillus suis showed the highest resistance levels among all identified species. AMR was positively correlated with both the duration and the number of antimicrobial agents used in feed, reinforcing the need for prudent AMU practices. The use of autogenous vaccines against Pasteurella multocida was associated with reduced lung lesions, underscoring the value of vaccination in disease control. AMR surveillance programs may benefit from including bacterial colonizers from the microbiota, though further studies are necessary to better understand the resistance dynamics of these commensals.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; metaphylaxis; nasal microbiota; swine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zeon O., Kibe L.W. Antimicrobial Drug Resistance and Antimicrobial Resistant Threats. Physician Assist. Clin. 2023;8:411–420. doi: 10.1016/j.cpha.2023.03.001. - DOI
-
- Letek M. Alexander Fleming, The discoverer of the antibiotic effects of penicillin. Front. Young Minds. 2020;8:159. doi: 10.3389/frym.2019.00159. - DOI
-
- Magiorakos A.-P., Srinivasan A., Carey R.B., Carmeli Y., Falagas M.E., Giske C.G., Harbarth S., Hindler J.F., Kahlmeter G., Olsson-Liljequist B., et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012;18:268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

