The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants
- PMID: 40572357
- PMCID: PMC12195260
- DOI: 10.3390/mi16060637
The Preparation of a GO/ZnO/nHAp Composite Coating and the Study of Its Performance Optimization for Pure Titanium Implants
Abstract
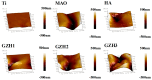
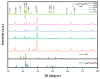
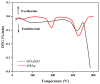
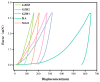
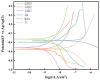
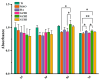
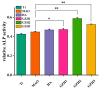
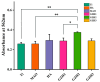
In this study, a graphene oxide (GO)/zinc oxide (ZnO)/hydroxyapatite (nHAp) composite coating was constructed on a pure titanium surface by microarc oxidation (MAO) pretreatment combined with hydrothermal technology (HT), thereby making it possible to explore the performance optimization of this coating for Ti-based implants. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), an energy dispersion spectrometer (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Ramam spectroscopy (Ramam), etc., confirmed that the GO/ZnO/nHAp composites were successfully loaded onto the pure Ti surfaces. Through nanoindentation, differential thermal analysis (DiamondTG/DTA), and dynamic polarization potential detection, the GO/ZnO/nHAp composite coating imparts excellent nanohardness (2.7 + 1.0 GPa), elastic modulus (53.5 + 1.0 GPa), thermal stability, and corrosion resistance to pure Ti implants; hemolysis rate analysis, CCK-8, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) detection, alizarin red staining, and other experiments further show that the coating improves the hemocompatibility, biocompatibility, and bone guidance of the Ti implant surface. Studies have shown that GO/ZnO/nHAp composite coatings can effectively optimize the mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and bone guidance of pure Ti implants, so that they can obtain an elastic modulus that matches human bone.
Keywords: GO/ZnO/nHAp composite coating; bone guidance; corrosion resistance; hydrothermal technology; microarc oxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures













Similar articles
-
[In vitro osteogenic performance study of graphene oxide-coated titanium surfaces modified with dopamine or silane].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 1;43(3):336-345. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2025.2024357. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40523813 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Surface modification of titanium implants with Mg-containing coatings to promote osseointegration.Acta Biomater. 2023 Oct 1;169:19-44. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.07.048. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37517617
-
Bioinspired Hierarchical PEEK and Amorphous Silicon Nitride Composite Coatings on Titanium Alloy Biomedical Implants.Small. 2025 Jul;21(26):e2410313. doi: 10.1002/smll.202410313. Epub 2025 May 13. Small. 2025. PMID: 40357807
-
Bio-functional azithromycin loaded polyvinyl alcohol and fucoidan hydrogel coating for titanium Implants: An experimental in vitro study.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025 Sep-Oct;15(5):1043-1050. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.07.011. Epub 2025 Jul 21. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2025. PMID: 40717741 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

