Eleutherococcus senticosus (Acanthopanax senticosus): An Important Adaptogenic Plant
- PMID: 40572479
- PMCID: PMC12195798
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30122512
Eleutherococcus senticosus (Acanthopanax senticosus): An Important Adaptogenic Plant
Abstract
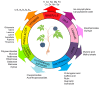
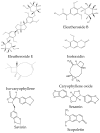
This comprehensive review focuses on Eleutherococcus senticosus (ES), examining the phytochemical composition, traditional medicinal roles, ecological traits, and pharmacological effects. Native to Northeast Asia, ES is used in traditional Chinese, Korean, and Japanese medicine. The rhizomes and bark are utilized medicinally and valued for their adaptogenic properties that enhance stress resistance, boost mental and physical endurance, and exhibit immunostimulatory effects that strengthen the immune system. Its pharmacological potential stems from a variety of bioactive compounds, including eleutherosides, lignans, saponins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides, which contribute to health benefits such as neuroprotective, antidiabetic, anticancer, and antioxidative activities. Neuroprotective properties may aid in the management of neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, while antidiabetic effects support glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity. With increasing demands and conservation concerns, sustainable cultivation practices are essential, as ES is endangered in some areas. Plant biotechnology techniques offer solutions to enhance secondary metabolite yields while ensuring genetic stability and minimizing environmental impacts. ES is a promising natural resource for various industries because of its extensive benefits. Still, its conservation and sustainable production are critical and require ongoing research and innovative cultivation strategies.
Keywords: Siberian ginseng; adaptogenic raw materials; biological activity; medicinal plants; phytochemical composition; utility of Eleutherococcus senticosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemical Composition and In Vitro Biological Activity of the Polar and Non-Polar Fractions Obtained from the Roots of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. et Maxim.) Maxim.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 12;26(12):5619. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125619. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565083 Free PMC article.
-
Botany, traditional usages, phytochemistry, pharmaceutical analysis, and pharmacology of Eleutherococcus nodiflorus (Dunn) S.Y.Hu: A systematic review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;306:116152. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116152. Epub 2023 Jan 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36641105
-
Ethnopharmacologically important highly subsidized Indian medicinal plants: Systematic review on their traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control, conservation status and future prospective.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Feb 10;320:117385. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117385. Epub 2023 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37951375
-
Recent Advances on the Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Properties, and Product Development of Morus alba.Phytochem Anal. 2025 Jul;36(5):1301-1332. doi: 10.1002/pca.3544. Epub 2025 May 30. Phytochem Anal. 2025. PMID: 40448298 Review.
-
Ethnobotanical Significance, Phytopharmacology, and Toxicological Profile of Limonia acidissima L. (Rutaceae): A Review.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(9):1459-1490. doi: 10.2174/0113862073285538240417051928. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38676498 Review.
References
-
- Gerontakos S., Taylor A., Avdeeva A.Y., Shikova V.A., Pozharitskaya O.N., Casteleijn D., Wardle J., Shikov A.N. Findings of Russian Literature on the Clinical Application of Eleutherococcussenticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.): A Narrative Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021;278:114274. - PubMed
-
- Flora of China Eleutherococcussenticosus. [(accessed on 4 January 2024)]. Available online: http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=220004653.
-
- Guo S., Wei H., Li J., Fan R., Xu M., Chen X., Wang Z. Geographical Distribution and Environmental Correlates of Eleutherosides and Isofraxidin in Eleutherococcussenticosus from Natural Populations in Forests at Northeast China. Forests. 2019;10:872. doi: 10.3390/f10100872. - DOI
-
- The World Flora Online’ WFO Eleutherococcussenticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim. 2024. [(accessed on 31 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000948117#B.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

